- Phân tích
- Tin tức và các công cụ
- Tin tức thị trường
- GBP/USD Price Analysis: At make or a break below 1.2700
GBP/USD Price Analysis: At make or a break below 1.2700
- GBP/USD posts a fresh monthly low near 1.2665 as the US Dollar recovers.
- The US Dollar bounces back on lower US jobless claims for the week ending August 2.
- The Cable extends its losing streak for the fourth trading day.
The GBP/USD pair hovers near a fresh monthly low around 1.2665 in Thursday’s American session. The Cable exhibits a subdued performance as the US Dollar (USD) has recovered sharply after the release of the lower-than-expected United States (US) Initial Jobless Claims in the week ending August 2.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, jumps to near 103.40 after recovering intraday losses. The US Department of Labor showed that individual claiming jobless benefits for the first time came in lower at 233K than estimates of 240K, and the prior release of 249K.
However, the near-term outlook of the US Dollar remains uncertain as soft jobless claims would be insufficient to negatively influence market speculation that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will cut interest rates by more than 100 basis points (bps) this year.
Meanwhile, the Pound Sterling (GBP) remains under pressure on global risk-aversion. The British currency will be influenced by market expectations for Bank of England (BoE) rate cuts amid an absence of top-tier United Kingdom (UK) economic data.
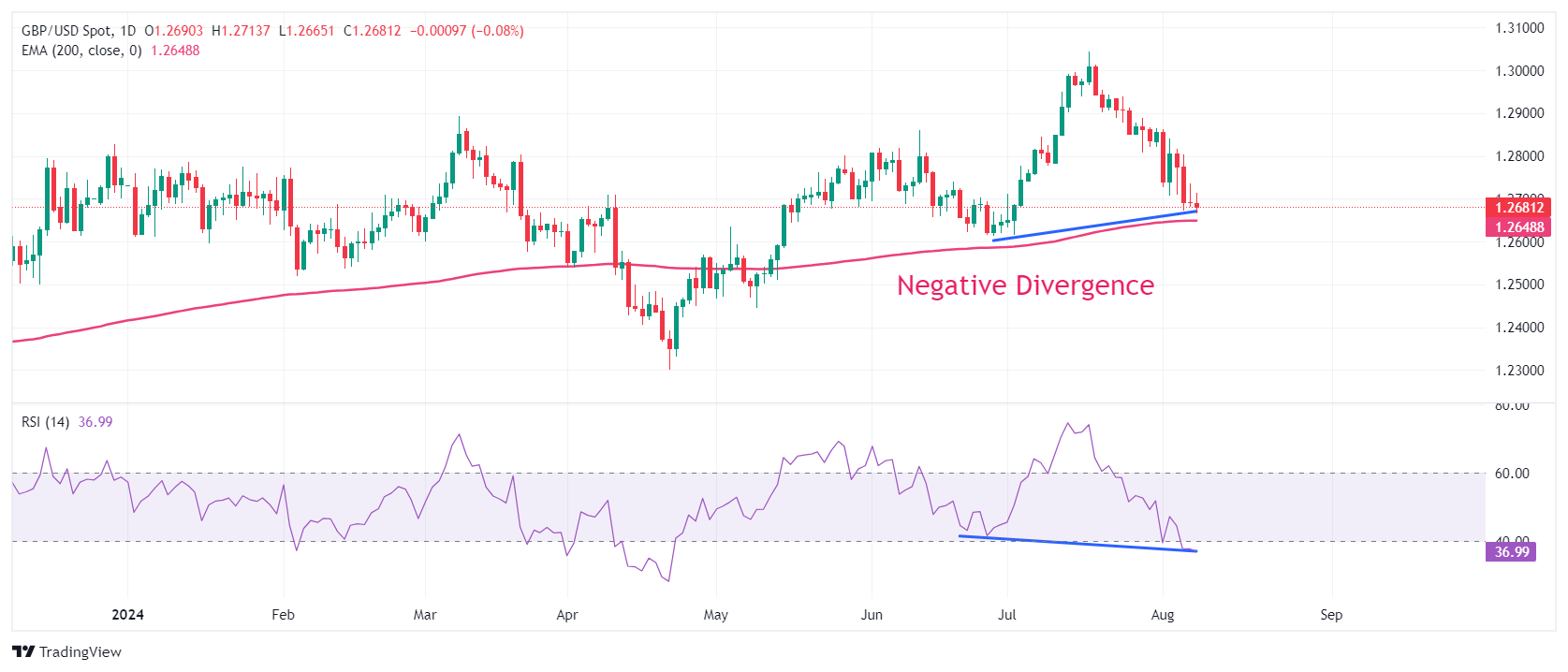
GBP/USD extends its losing spree for the fourth trading session on Thursday. The Cable is at a make or a break below the crucial figure of 1.2700. The major exhibits a Negative divergence formation on a daily timeframe in which the asset continues to build higher lows, while the momentum oscillator makes lower lows. This generally results in a bullish reversal but it should be confirmed with more indicators.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) formed a fresh lower swing at 37.00, which suggests that the bearish momentum is still intact.
The asset still holds the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.2650.
More downside could appear if the asset breaks below the intraday low of 1.2665. This would expose the asset to June 27 low at 1.2613, followed by April 29 high at 1.2570.
On the flip side, a recovery move above August 6 high at 1.2800 would drive the asset towards August 2 high at 1.2840 and the round-level resistance of 1.2900.
GBP/USD daily chart
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, aka ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
© 2000-2026. Bản quyền Teletrade.
Trang web này được quản lý bởi Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Thông tin trên trang web không phải là cơ sở để đưa ra quyết định đầu tư và chỉ được cung cấp cho mục đích làm quen.
Giao dịch trên thị trường tài chính (đặc biệt là giao dịch sử dụng các công cụ biên) mở ra những cơ hội lớn và tạo điều kiện cho các nhà đầu tư sẵn sàng mạo hiểm để thu lợi nhuận, tuy nhiên nó mang trong mình nguy cơ rủi ro khá cao. Chính vì vậy trước khi tiến hành giao dịch cần phải xem xét mọi mặt vấn đề chấp nhận tiến hành giao dịch cụ thể xét theo quan điểm của nguồn lực tài chính sẵn có và mức độ am hiểu thị trường tài chính.
Sử dụng thông tin: sử dụng toàn bộ hay riêng biệt các dữ liệu trên trang web của công ty TeleTrade như một nguồn cung cấp thông tin nhất định. Việc sử dụng tư liệu từ trang web cần kèm theo liên kết đến trang teletrade.vn. Việc tự động thu thập số liệu cũng như thông tin từ trang web TeleTrade đều không được phép.
Xin vui lòng liên hệ với pr@teletrade.global nếu có câu hỏi.