- Phân tích
- Tin tức và các công cụ
- Tin tức thị trường
- Japanese Yen declines further as BoJ Uchida refuses to raise rates amid market instability
Japanese Yen declines further as BoJ Uchida refuses to raise rates amid market instability
- The Japanese Yen continues to lose ground following the dovish remarks from BoJ Deputy Governor Shinichi Uchida.
- BoJ’s Uchida emphasized that the central bank must maintain its current level of monetary easing for the time being.
- CME FedWatch tool suggests 67.5% odds of a 50-basis point Fed rate cut in September, up from 13.2% last week.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) extends its losses against the US Dollar (USD) for the second successive day. This downside could be attributed to the comments from Bank of Japan (BoJ) Deputy Governor Shinichi Uchida on Wednesday, “We won’t raise rates when markets are unstable,” according to Reuters.
Deputy Governor Uchida also noted that the BoJ's interest rate strategy will adapt if market volatility alters economic forecasts, risk assessments, or projections. Given recent market volatility, he emphasized the need for careful monitoring of the economic and price impacts of their policies, stating, “We must maintain the current degree of monetary easing for the time being.”
The upside potential for the USD/JPY pair may be limited as the US Dollar faces challenges, with markets anticipating a more substantial rate cut beginning in September. According to the CME FedWatch tool, there is now a 67.5% probability of a 50-basis point (bps) interest rate cut by the US Federal Reserve (Fed) in September, up from 13.2% a week earlier.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Japanese Yen weakens following remarks from BoJ’s Uchida
- Japan’s Chief Cabinet Secretary Yoshimasa Hayashi stated on Tuesday that “wage increases are expected to extend to part-timers and small businesses by autumn, supported by strong Shunto results and minimum wage hikes.” Hayashi did not provide comments on foreign exchange levels.
- Japan’s Labor Cash Earnings data showed a 4.5% year-on-year increase in average income for June, surpassing both the previous 2.0% and the expected 2.3% readings. This is the highest increase since January 1997, reinforcing Japan's transition toward a rising interest rate environment.
- According to Reuters, Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco President Mary Daly expressed increased confidence on Monday that US inflation is moving towards the Fed's 2% target. Daly noted that “risks to the Fed's mandates are becoming more balanced and that there is openness to the possibility of cutting rates in upcoming meetings.”
- Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee stated on Monday that the US central bank is prepared to act if economic or financial conditions worsen. Goolsbee emphasized, "We're forward-looking about it, and so if the conditions collectively start coming in like that on the through line, there’s deterioration on any of those parts, we’re going to fix it.” according to Reuters.
- The minutes from the Bank of Japan's June meeting showed that some members expressed concerns about rising import prices due to the recent decline in the JPY, which could pose an upside risk to inflation. One member noted that cost-push inflation might intensify underlying inflation if it results in higher inflation expectations and wage increases.
- The Bank of Japan (BoJ) released the full version of its Quarterly Outlook Report on Thursday, noting that there is a possibility wages and inflation could exceed expectations. This could be accompanied by rising inflation expectations and a tight labor market.
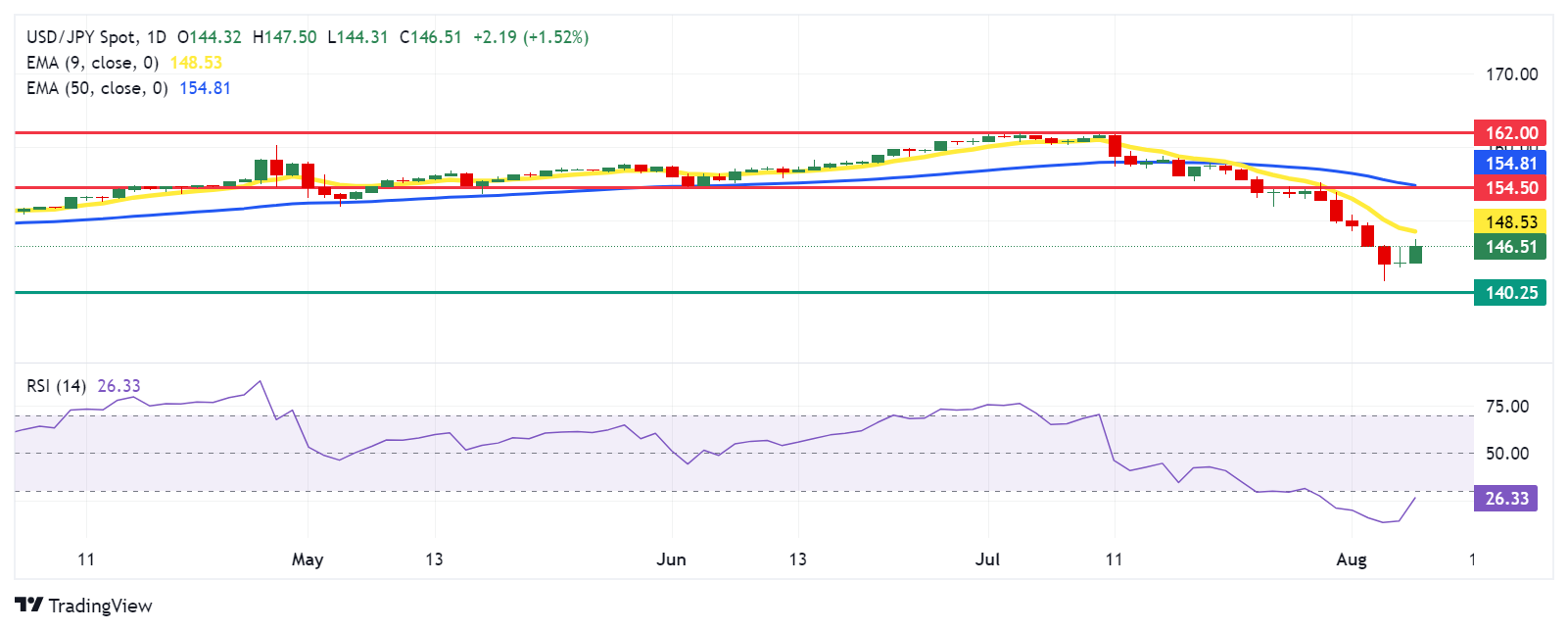
Technical Analysis: USD/JPY rises to near 146.50
USD/JPY trades around 146.70 on Wednesday. The daily chart analysis shows that the pair continues to rise toward the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 148.57 level, suggesting a weakening of the bearish momentum. Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is below 30, signaling that the currency pair is oversold and could see a short-term rebound.
Regarding support, the USD/JPY pair may test the throwback support at the 140.25 level, which was recorded in December.
In terms of resistance, the USD/JPY pair might face a barrier at the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 149.22. A breakout above this level could reduce bearish momentum and enable the pair to test the "throwback support turned resistance" at 154.50, followed by the 50-day EMA at 155.58.
USD/JPY: Daily Chart
Japanese Yen PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Japanese Yen (JPY) against listed major currencies today. Japanese Yen was the weakest against the New Zealand Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.14% | -0.13% | 1.70% | -0.04% | -0.37% | -0.88% | 0.59% | |
| EUR | -0.14% | -0.27% | 1.60% | -0.18% | -0.54% | -1.02% | 0.47% | |
| GBP | 0.13% | 0.27% | 1.85% | 0.08% | -0.28% | -0.70% | 0.72% | |
| JPY | -1.70% | -1.60% | -1.85% | -1.73% | -2.09% | -2.54% | -1.12% | |
| CAD | 0.04% | 0.18% | -0.08% | 1.73% | -0.34% | -0.80% | 0.64% | |
| AUD | 0.37% | 0.54% | 0.28% | 2.09% | 0.34% | -0.42% | 1.01% | |
| NZD | 0.88% | 1.02% | 0.70% | 2.54% | 0.80% | 0.42% | 1.43% | |
| CHF | -0.59% | -0.47% | -0.72% | 1.12% | -0.64% | -1.01% | -1.43% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Japanese Yen from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent JPY (base)/USD (quote).
Bank of Japan FAQs
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) is the Japanese central bank, which sets monetary policy in the country. Its mandate is to issue banknotes and carry out currency and monetary control to ensure price stability, which means an inflation target of around 2%.
The Bank of Japan has embarked in an ultra-loose monetary policy since 2013 in order to stimulate the economy and fuel inflation amid a low-inflationary environment. The bank’s policy is based on Quantitative and Qualitative Easing (QQE), or printing notes to buy assets such as government or corporate bonds to provide liquidity. In 2016, the bank doubled down on its strategy and further loosened policy by first introducing negative interest rates and then directly controlling the yield of its 10-year government bonds.
The Bank’s massive stimulus has caused the Yen to depreciate against its main currency peers. This process has exacerbated more recently due to an increasing policy divergence between the Bank of Japan and other main central banks, which have opted to increase interest rates sharply to fight decades-high levels of inflation. The BoJ’s policy of holding down rates has led to a widening differential with other currencies, dragging down the value of the Yen.
A weaker Yen and the spike in global energy prices have led to an increase in Japanese inflation, which has exceeded the BoJ’s 2% target. With wage inflation becoming a cause of concern, the BoJ looks to move away from ultra loose policy, while trying to avoid slowing the activity too much.
© 2000-2026. Bản quyền Teletrade.
Trang web này được quản lý bởi Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Thông tin trên trang web không phải là cơ sở để đưa ra quyết định đầu tư và chỉ được cung cấp cho mục đích làm quen.
Giao dịch trên thị trường tài chính (đặc biệt là giao dịch sử dụng các công cụ biên) mở ra những cơ hội lớn và tạo điều kiện cho các nhà đầu tư sẵn sàng mạo hiểm để thu lợi nhuận, tuy nhiên nó mang trong mình nguy cơ rủi ro khá cao. Chính vì vậy trước khi tiến hành giao dịch cần phải xem xét mọi mặt vấn đề chấp nhận tiến hành giao dịch cụ thể xét theo quan điểm của nguồn lực tài chính sẵn có và mức độ am hiểu thị trường tài chính.
Sử dụng thông tin: sử dụng toàn bộ hay riêng biệt các dữ liệu trên trang web của công ty TeleTrade như một nguồn cung cấp thông tin nhất định. Việc sử dụng tư liệu từ trang web cần kèm theo liên kết đến trang teletrade.vn. Việc tự động thu thập số liệu cũng như thông tin từ trang web TeleTrade đều không được phép.
Xin vui lòng liên hệ với pr@teletrade.global nếu có câu hỏi.