- Phân tích
- Tin tức và các công cụ
- Tin tức thị trường
- USD/INR remains steady amid rising US bond yields, Fed rate cut bets
USD/INR remains steady amid rising US bond yields, Fed rate cut bets
- Indian Rupee trades sideways on Tuesday amid a cautious mood.
- Higher US bond yields and lower bets on Fed rate cuts might drag the INR lower against the US Dollar.
- The respective Indian and US Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation data are due on Wednesday ahead of the Fed rate decision.
Indian Rupee (INR) remains flat on Tuesday despite the firmer US Dollar (USD). The rising US bond yields and lower bets on rate cuts from the Federal Reserve (Fed) after stronger-than-expected US employment data lift the Greenback for the time being. Nonetheless, the lower crude oil prices and easing political uncertainties surrounding India’s election might support the INR and cap the upside for the pair. Additionally, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to intervene in the market to prevent the Indian Rupee from depreciating.
Market players will keep an eye on India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI), which is due on Wednesday. On the US docket, the May CPI will be released ahead of the Fed interest rate decision. After the Fed meeting, the US central bank will update the Summary of Economic Projections (SEP). Any hawkish message from Fed officials is likely to boost the Greenback against its rivals.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Indian Rupee awaits the fresh catalysts
- The INR closed at 83.5050 against the US Dollar, down 0.1% from its close at 83.3725 in the previous session.
- India is estimated to expand at 7% in FY25 as the post-pandemic recovery in the capital expenditure (capex) cycle, fueled by government spending and robust residential real estate demand, said Tanvee Gupta Jain, chief India economist at UBS Securities.
- "We expect the rupee to trade with a slight negative bias on strong US Dollar amid rising expectations of a delay in interest rate cut by the US Federal Reserve due to tight job market," said BNP Paribas Research Analyst Anuj Choudhary.
- Financial markets have priced in a nearly 47% chance of a Fed rate cut for the September meeting, down from 68% before the NFP data, according to the CME FedWatch tool.
- The US headline CPI figure is expected to show an increase of 3.4% YoY in May, while core CPI is estimated to rise 3.5% YoY in the same report period.
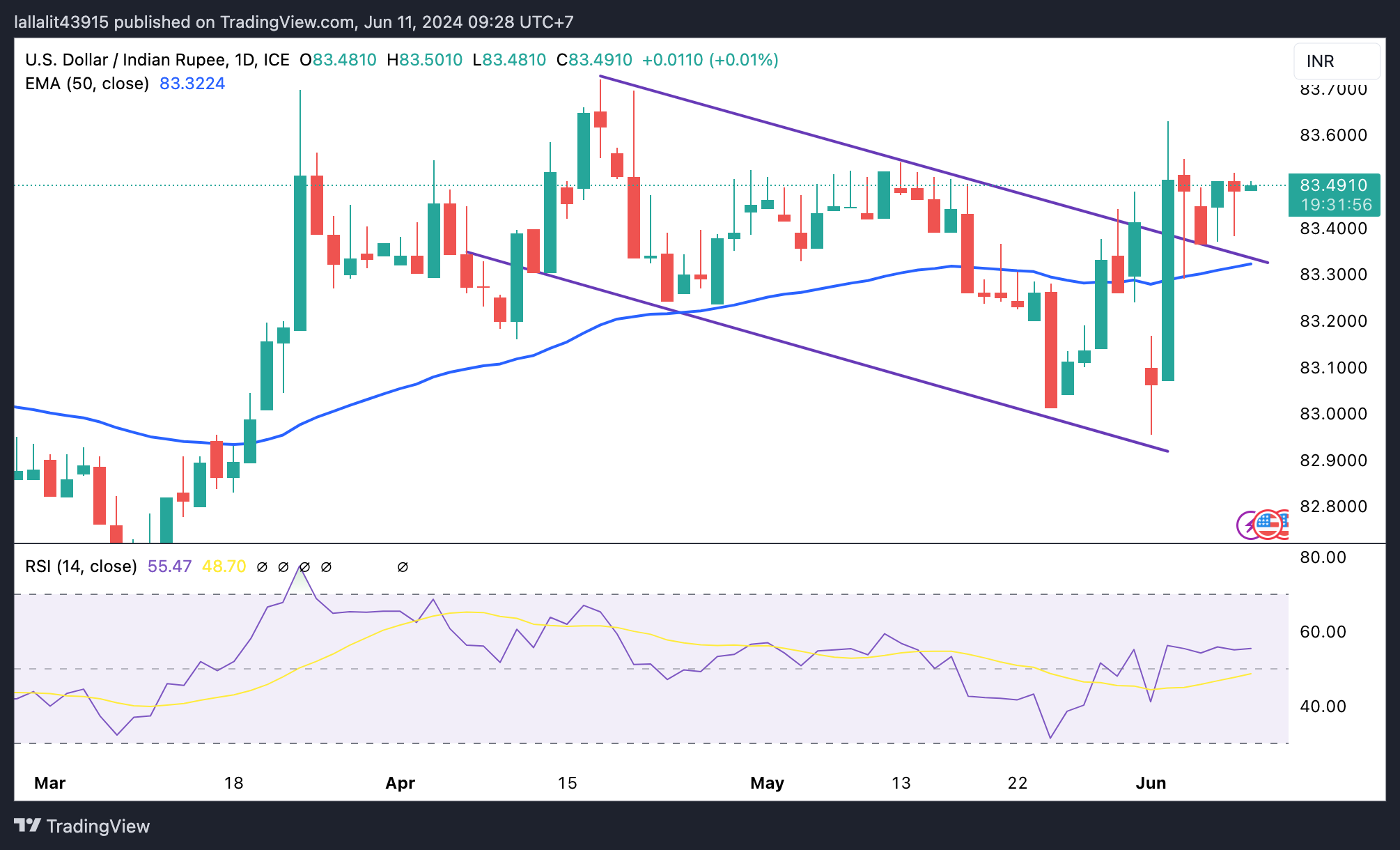
Technical analysis: USD/INR maintains a constructive outlook in the longer term
The Indian Rupee trades flat on the day. The USD/INR pair keeps the bullish vibe unchanged on the daily timeframe while holding above the descending trend channel upper boundary and the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
In the near term, the extended consolidation phase is likely to continue since the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) hovers lower towards the 50-midline.
Any follow-through buying above 83.55, a high of June 5, will pave the way to 83.72, a high of April 17. Extended gains will see a rally to the 84.00 psychological level.
On the downside, the first downside target is seen at the 83.30–83.35 region, portraying the resistance-turned-support level and the 100-day EMA. A breach of this level will expose the 83.00 round level, followed by 82.78, a low of January 15.
US Dollar price today
The table below shows the percentage change of US Dollar (USD) against listed major currencies today. US Dollar was the strongest against the Australian Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | CAD | AUD | JPY | NZD | CHF | |
| USD | -0.05% | -0.04% | 0.04% | 0.21% | 0.11% | 0.09% | 0.01% | |
| EUR | 0.04% | -0.02% | 0.09% | 0.28% | 0.17% | 0.14% | 0.05% | |
| GBP | 0.06% | 0.02% | 0.10% | 0.27% | 0.17% | 0.17% | 0.06% | |
| CAD | -0.03% | -0.08% | -0.08% | 0.19% | 0.08% | 0.06% | -0.03% | |
| AUD | -0.23% | -0.27% | -0.27% | -0.18% | -0.10% | -0.12% | -0.22% | |
| JPY | -0.12% | -0.16% | -0.17% | -0.07% | 0.12% | -0.03% | -0.12% | |
| NZD | -0.09% | -0.16% | -0.18% | -0.05% | 0.12% | 0.00% | -0.09% | |
| CHF | 0.00% | -0.05% | -0.06% | 0.04% | 0.20% | 0.10% | 0.10% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/JPY (quote).
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
© 2000-2026. Bản quyền Teletrade.
Trang web này được quản lý bởi Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Thông tin trên trang web không phải là cơ sở để đưa ra quyết định đầu tư và chỉ được cung cấp cho mục đích làm quen.
Giao dịch trên thị trường tài chính (đặc biệt là giao dịch sử dụng các công cụ biên) mở ra những cơ hội lớn và tạo điều kiện cho các nhà đầu tư sẵn sàng mạo hiểm để thu lợi nhuận, tuy nhiên nó mang trong mình nguy cơ rủi ro khá cao. Chính vì vậy trước khi tiến hành giao dịch cần phải xem xét mọi mặt vấn đề chấp nhận tiến hành giao dịch cụ thể xét theo quan điểm của nguồn lực tài chính sẵn có và mức độ am hiểu thị trường tài chính.
Sử dụng thông tin: sử dụng toàn bộ hay riêng biệt các dữ liệu trên trang web của công ty TeleTrade như một nguồn cung cấp thông tin nhất định. Việc sử dụng tư liệu từ trang web cần kèm theo liên kết đến trang teletrade.vn. Việc tự động thu thập số liệu cũng như thông tin từ trang web TeleTrade đều không được phép.
Xin vui lòng liên hệ với pr@teletrade.global nếu có câu hỏi.















