- Phân tích
- Tin tức và các công cụ
- Tin tức thị trường
- Mexican Peso under pressure ahead of expected Banxico rate cut
Mexican Peso under pressure ahead of expected Banxico rate cut
- Mexican Peso weakens as investors eye Banxico policy decision on Thursday.
- Mexico’s retail sales data indicate cautious consumer spending, setting stage for Banxico's potential 25 bps rate cut.
- Banxico rate cut may shrink US-Mexico rate gap, possibly nudging USD/MXN near 17.00.
- Decision might not be unanimous as Deputy Governors Espinosa and Heath expressed concerns over persistent inflation.
The Mexican Peso begins the session on the defensive against the US Dollar as investors prepare for the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) monetary policy decision. Most analysts expect a 25-basis-point rate cut, which would lower reference rates to 11.00%. The USD/MXN pair exchanges hands at a 16.74 for a gain of 0.4%.
Mexico’s economic docket featured retail sales for February, which improved on a monthly basis, yet suggests consumers are spending less. In the 12 months to January, sales missed estimates and plunged sharply. Later at 19:00 GMT, the Banxico Governing Council led by Governor Victoria Rodriguez Ceja will likely cut rates for the first time since mid-2021.
The decision is expected to be split, as two Deputy Governors, Irene Espinosa and Jonathan Heath, expressed their disagreement with easing policy, adding that inflation remains high and stubbornly stickier than expected. Although February’s inflation cooled from 4.88% to 4.40% and core figures decreased from 4.76% to 4.64%, external factors could trigger a second wave of inflation.
In the meantime, traders continued to digest the latest monetary policy decision by the Federal Reserve, which held rates unchanged and kept their projections for three 25 bps rate cuts toward year end. Although revising the federal funds rate (FFR) level upward to 3.9%, the Fed’s decision was perceived as dovish.
Given the backdrop, if Banxico lowers rates, that would decrease the interest rate spread between the US and Mexico, bolstering the USD/MXN, which could hit 17.00 following the decision.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso weakens as reduction of rate differentials looms
- Mexico’s Retail Sales fell -0.6% MoM in January, missing estimates of 0.4% expansion but better than December’s data. Yearly figures plummeted from -0.2% to -0.8%, smashing projections for a 1.2% expansion.
- Mexico’s economic data released in the week:
- Aggregate Demand rose by 0.3% QoQ in Q4, up from 0%. On an annual basis, it decelerated from 2.7% to 2.6%.
- Private Spending on a quarterly basis slowed from 1.2% to 0.9%. On a yearly basis, it improved from 4.3% to 5.1%.
- The slowdown in Mexico’s economy is one of the main reasons that Banxico is eyeing the first cut. Mexico’s central bank expects the economy to grow 2.8% YoY in 2024, down from 3%, but maintains its 1.5% prior call for 2025.
- The US economic schedule revealed that Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending March 16 rose by 210K, below estimates of 215K and the prior week’s figures.
- S&P Global PMI figures for the United States were mixed, with Services and Composite PMI readings cooling but remaining in expansionary territory. The S&P Global Manufacturing PMI was the outlier, exceeding estimates of 51.7 and the previous reading of 52.2 by jumping to 52.5.
- Existing Home Sales rose by 9.5% from 4 million to 4.38 million.
- The latest inflation figures in the United States prompted investors to price in a less dovish stance. Money market futures have adjusted their rate cut expectations to be more in line with the Fed's as they foresee theFFR at 4.71% toward the end of the year. Analysts estimate the Fed will not change its FFR level until June or later.
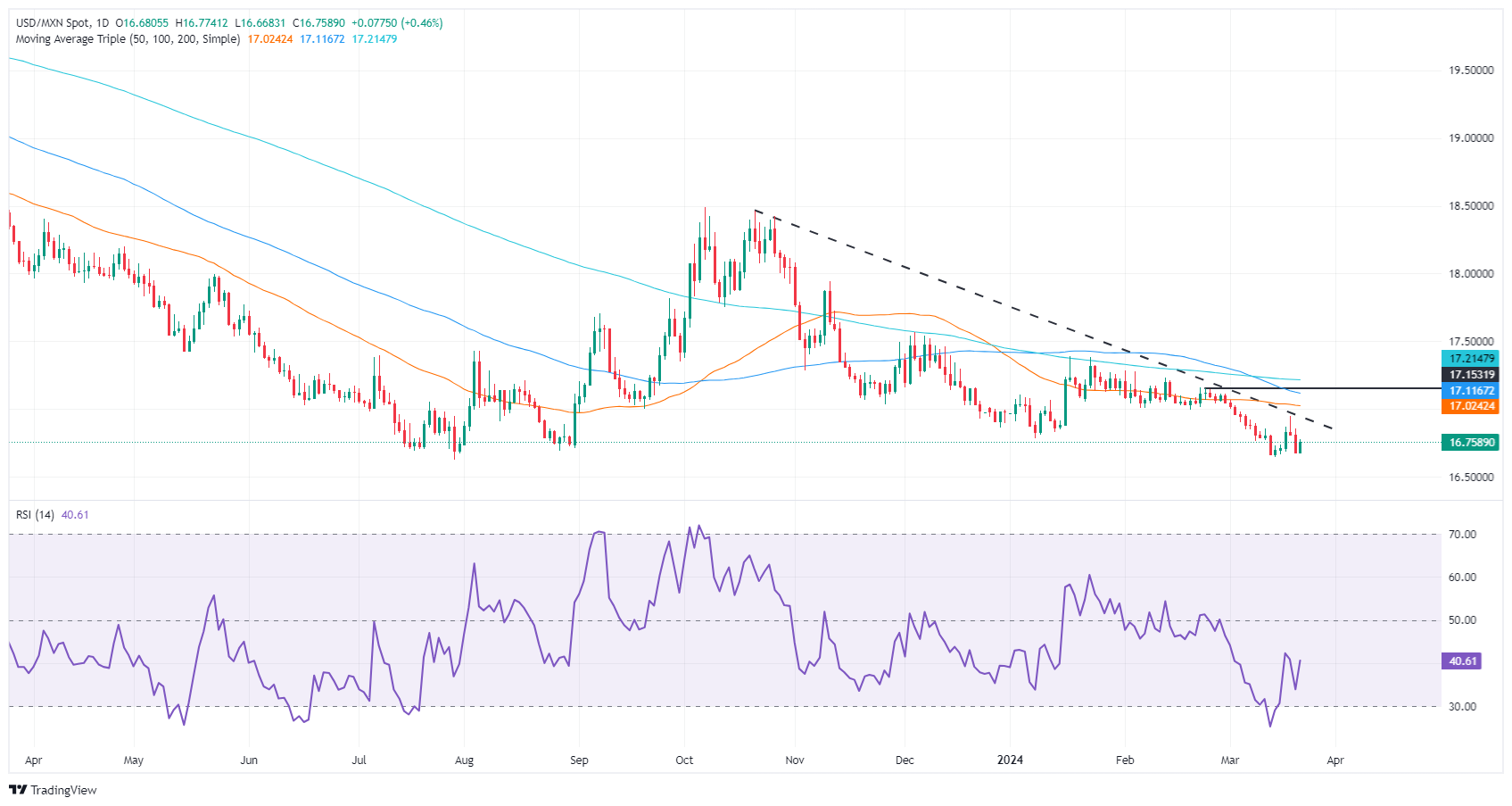
Technical analysis: Mexican Peso treads water as USD/MXN accelerates to 16.80
As mentioned on Wednesday, “the USD/MXN is neutral to downwardly biased after buyers lifted the exchange rate to a weekly high of 16.94 before retreating beneath 16.80.” However, with the Mexican Central Bank decision looming, a quarter percentage rate cut could lift the exotic pair and break key resistance levels.
The first resistance would be the March 19 cycle high at 16.94, followed by the psychological 17.00 figure. Up next would be a busy area of dynamic supply zones, led by the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 17.01, the 100-day SMA at 17.12 and the 200-day SMA at 17.20.
On the other hand, sellers must drag the exchange rate below the current year-to-date low of 16.64 before challenging last year’s low of 16.62.
USD/MXN Price Action – Daily Chart
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.
© 2000-2026. Bản quyền Teletrade.
Trang web này được quản lý bởi Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Thông tin trên trang web không phải là cơ sở để đưa ra quyết định đầu tư và chỉ được cung cấp cho mục đích làm quen.
Giao dịch trên thị trường tài chính (đặc biệt là giao dịch sử dụng các công cụ biên) mở ra những cơ hội lớn và tạo điều kiện cho các nhà đầu tư sẵn sàng mạo hiểm để thu lợi nhuận, tuy nhiên nó mang trong mình nguy cơ rủi ro khá cao. Chính vì vậy trước khi tiến hành giao dịch cần phải xem xét mọi mặt vấn đề chấp nhận tiến hành giao dịch cụ thể xét theo quan điểm của nguồn lực tài chính sẵn có và mức độ am hiểu thị trường tài chính.
Sử dụng thông tin: sử dụng toàn bộ hay riêng biệt các dữ liệu trên trang web của công ty TeleTrade như một nguồn cung cấp thông tin nhất định. Việc sử dụng tư liệu từ trang web cần kèm theo liên kết đến trang teletrade.vn. Việc tự động thu thập số liệu cũng như thông tin từ trang web TeleTrade đều không được phép.
Xin vui lòng liên hệ với pr@teletrade.global nếu có câu hỏi.