- Аналітика
- Новини та інструменти
- Новини ринків
- AUD/JPY rises on speculation surrounding the RBA raising policy rate
AUD/JPY rises on speculation surrounding the RBA raising policy rate
- The Australian Dollar surges driven by growing hawkish sentiment surrounding RBA, following the hot CPI data.
- Judo Bank chief economic adviser Warren Hogan predicts that the RBA might increase the cash rate three times in 2024.
- The safe-haven JPY loses ground due to the uncertainty surrounding the BoJ's rate outlook.
AUD/JPY continues its winning streak for the sixth successive session on Monday, hovering around 104.50, a level not seen since April 2013. The persistent upward momentum of the AUD/JPY pair is driven by the increasing hawkish sentiment surrounding the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA), following the release of last week's Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation data.
The unexpected surge in inflation figures prompted economists to revise their earlier forecasts significantly. Warren Hogan, chief economic adviser at Judo Bank, told “The Australian Financial Review” his anticipation of the central bank raising the cash rate three times this year, reaching 5.1%, with the first hike likely in August. Investors now look forward to Retail Sales for March on Tuesday, which gauges Australia’s consumer spending. It has a significant bearing on Australia’s inflation and GDP.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) tumbled to new multi-decade lows following the Bank of Japan's (BoJ) decision to maintain policy settings unchanged on Friday. Uncertainty surrounding the BoJ's rate outlook, indications of cooling inflation in Japan, and a generally optimistic sentiment in equity markets are pivotal factors eroding the safe-haven appeal of the JPY.
Furthermore, expectations for a prolonged wide interest rate differential between Japan and the other countries imply that the JPY's trajectory is biased towards further decline. With Japanese markets closed on Monday for Showa Day, market dynamics may see limited shifts in the absence of trading activity.
Daily Digest Market Movers: AUD/JPY rises on increasing hawkish sentiment surrounding RBA
- Australia's stock market experienced a robust rally on Monday, inspired by a strong performance on Wall Street. The ASX 200 Index recovered some ground lost on Friday, with all 11 industry sectors trading in positive territory. Friday's rally on Wall Street was fueled by impressive earnings reports from tech giants such as Microsoft and Google's parent company, Alphabet, propelling the Nasdaq up by more than 2%
- On Friday, TD Securities' revision suggests a postponement of the anticipated rate cut by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) until February 2025, shifting from the previously anticipated date in November. This development strengthens the Australian Dollar (AUD) and, in turn, bolsters the AUD/JPY pair.
- BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda provided insights into the central bank's decision to maintain the status quo during the post-policy meeting press conference on Friday. Ueda outlined that the BoJ will adjust the degree of monetary easing if the underlying inflation rate rises. Additionally, He emphasized that easy financial conditions will be maintained for the time being, indicating the BoJ's commitment to supporting economic recovery and stability through accommodative monetary measures.
- Tokyo Consumer Price Index rose 1.8% YoY in April, well below the previous print of 2.6%. Markets were broadly expecting Tokyo inflation to hold steady over the period. The Core CPI fell sharply to 1.6% year-on-year, marking its lowest level since March 2022 and falling well below forecasts of 2.2%.
- On Friday, a report from Reuters said that the Bank of Japan (BOJ) is expected to project that inflation will remain close to its 2% target in the coming years and signal its preparedness to raise interest rates from their near-zero levels. This stance by the BOJ is aimed at preventing Yen depreciation and discouraging market participants from pushing the currency to fresh 34-year lows.
- Australia’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) increased to an all-time high of 137.40 points in the first quarter of 2024 from 136.10 points in the fourth quarter of 2023.
- As reported by the Japan Times, the percentage of Japanese companies aiming to raise their pay scales has surged to 70.7%, representing a notable increase of 6.3 percentage points compared to the prior year. Furthermore, the number of companies intending to implement pay-scale hikes and regular pay increases totaling 5% or higher has nearly doubled from the previous year, reaching 36.5%. This trend holds the potential to enhance the purchasing power of individuals, potentially leading to an uptick in consumer prices.
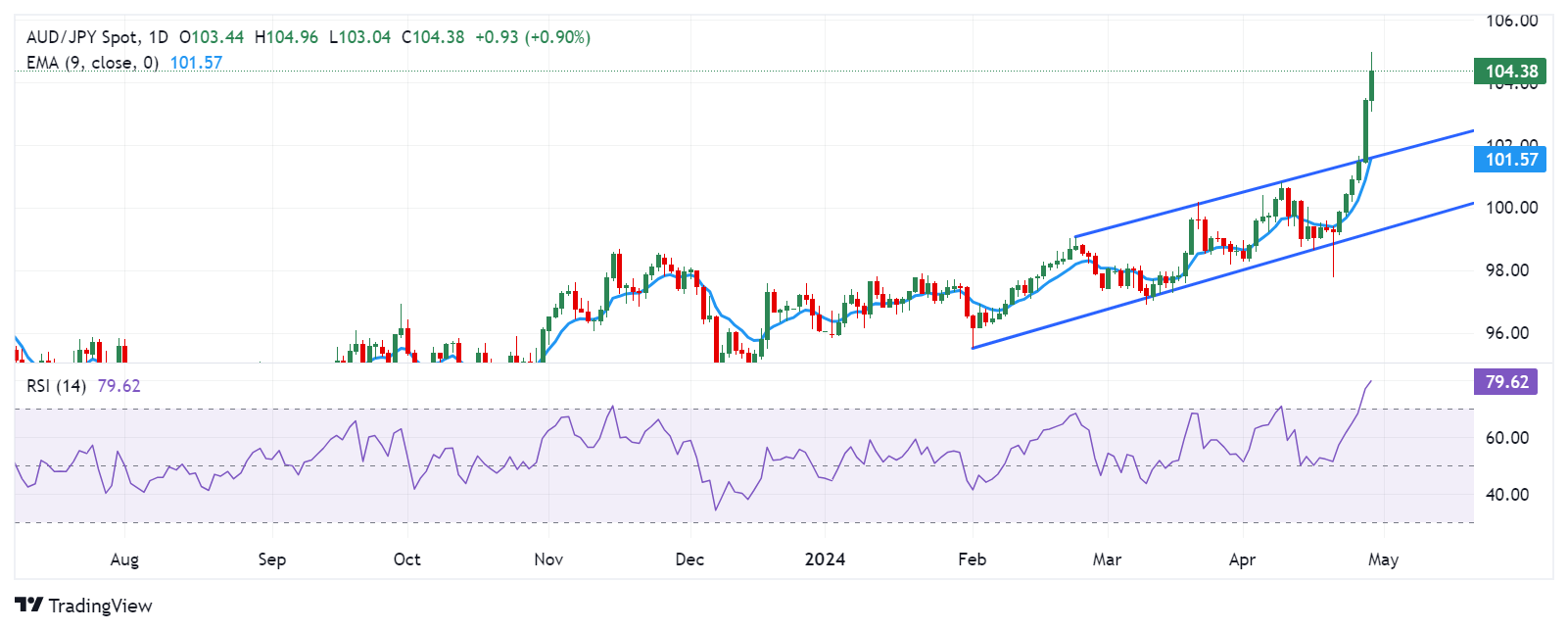
Technical Analysis: AUD/JPY surges to the major level of 104.50
The AUD/JPY trades around 104.50 on Monday, surpassing the upper boundary of the daily ascending channel. Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is trending above the 50-level, strengthening the bullish sentiment. The immediate resistance is seen at the psychological level of 105.00. A breakthrough above this level could support the cross to test the highest level of 105.43 recorded in April 2013.
On the downside, immediate support for the AUD/JPY pair could be found at the psychological level of 104.00. If the pair breaches below this level, the AUD/JPY cross could lead to a further decline toward the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 101.59, aligned with the lower boundary of the ascending channel and a major level of 101.50.
AUD/JPY: Daily Chart
Australian Dollar price today
The table below shows the percentage change of the Australian Dollar (AUD) against listed major currencies today. The Australian Dollar was the strongest against the Japanese Yen.
| USD | EUR | GBP | CAD | AUD | JPY | NZD | CHF | |
| USD | -0.07% | -0.11% | -0.05% | -0.28% | 0.55% | -0.23% | -0.12% | |
| EUR | 0.07% | -0.04% | 0.01% | -0.21% | 0.61% | -0.15% | -0.04% | |
| GBP | 0.12% | 0.04% | 0.06% | -0.16% | 0.67% | -0.12% | 0.01% | |
| CAD | 0.05% | -0.02% | -0.06% | -0.22% | 0.61% | -0.18% | -0.08% | |
| AUD | 0.28% | 0.20% | 0.16% | 0.22% | 0.83% | 0.05% | 0.16% | |
| JPY | -0.63% | -0.71% | -0.76% | -0.69% | -0.94% | -0.87% | -0.76% | |
| NZD | 0.23% | 0.15% | 0.10% | 0.17% | -0.05% | 0.77% | 0.11% | |
| CHF | 0.13% | 0.06% | 0.00% | 0.06% | -0.16% | 0.66% | -0.11% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/JPY (quote).
Australian Dollar FAQs
One of the most significant factors for the Australian Dollar (AUD) is the level of interest rates set by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA). Because Australia is a resource-rich country another key driver is the price of its biggest export, Iron Ore. The health of the Chinese economy, its largest trading partner, is a factor, as well as inflation in Australia, its growth rate, and Trade Balance. Market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe havens (risk-off) – is also a factor, with risk-on positive for AUD.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) influences the Australian Dollar (AUD) by setting the level of interest rates that Australian banks can lend to each other. This influences the level of interest rates in the economy as a whole. The main goal of the RBA is to maintain a stable inflation rate of 2-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively high interest rates compared to other major central banks support the AUD, and the opposite for relatively low. The RBA can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former AUD-negative and the latter AUD-positive.
China is Australia’s largest trading partner so the health of the Chinese economy is a major influence on the value of the Australian Dollar (AUD). When the Chinese economy is doing well it purchases more raw materials, goods and services from Australia, lifting demand for the AUD, and pushing up its value. The opposite is the case when the Chinese economy is not growing as fast as expected. Positive or negative surprises in Chinese growth data, therefore, often have a direct impact on the Australian Dollar and its pairs.
Iron Ore is Australia’s largest export, accounting for $118 billion a year according to data from 2021, with China as its primary destination. The price of Iron Ore, therefore, can be a driver of the Australian Dollar. Generally, if the price of Iron Ore rises, AUD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Iron Ore falls. Higher Iron Ore prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance for Australia, which is also positive of the AUD.
The Trade Balance, which is the difference between what a country earns from its exports versus what it pays for its imports, is another factor that can influence the value of the Australian Dollar. If Australia produces highly sought after exports, then its currency will gain in value purely from the surplus demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase its exports versus what it spends to purchase imports. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens the AUD, with the opposite effect if the Trade Balance is negative.
© 2000-2026. Уcі права захищені.
Cайт знаходитьcя під керуванням TeleTrade DJ. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Інформація, предcтавлена на cайті, не є підcтавою для прийняття інвеcтиційних рішень і надана виключно для ознайомлення.
Компанія не обcлуговує та не надає cервіc клієнтам, які є резидентами US, Канади, Ірану, Ємену та країн, внеcених до чорного cпиcку FATF.
Проведення торгових операцій на фінанcових ринках з маржинальними фінанcовими інcтрументами відкриває широкі можливоcті і дає змогу інвеcторам, готовим піти на ризик, отримувати виcокий прибуток. Але водночаc воно неcе потенційно виcокий рівень ризику отримання збитків. Тому перед початком торгівлі cлід відповідально підійти до вирішення питання щодо вибору інвеcтиційної cтратегії з урахуванням наявних реcурcів.
Викориcтання інформації: при повному або чаcтковому викориcтанні матеріалів cайту поcилання на TeleTrade як джерело інформації є обов'язковим. Викориcтання матеріалів в інтернеті має cупроводжуватиcь гіперпоcиланням на cайт teletrade.org. Автоматичний імпорт матеріалів та інформації із cайту заборонено.
З уcіх питань звертайтеcь за адреcою pr@teletrade.global.