- Аналітика
- Новини та інструменти
- Новини ринків
- Australian Dollar hovers below a psychological level amid a softer Aussie GDP
Australian Dollar hovers below a psychological level amid a softer Aussie GDP
- Australian Dollar extends losses as ASX 200 Index loses ground for third consecutive session.
- Australian GDP (QoQ) grew by 0.2%, slightly below the expected 0.3% in the fourth quarter of 2023.
- ISM Services PMI declined to 52.6 against the forecasted 53.0 for February.
- US Dollar gains ground on higher US Treasury yields.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) continues its decline for the third consecutive session on Wednesday, facing downward pressure amid a weaker equity market. The S&P/ASX 200 Index has declined for three consecutive sessions, mirroring the sell-off in technology stocks on Wall Street and lower mining stocks.
Australian Dollar remains largely unaffected by the softer-than-expected Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data. The GDP grew by 0.2% quarter-on-quarter in the fourth quarter of 2023, slightly below market expectations of no change at 0.3%. However, on a year-on-year basis, GDP expanded by 1.5%, surpassing the expected 1.4%, but falling short of the previous growth of 2.1%.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) continues to monitor the economy for signs of a slowdown, aiming to bring inflation back to target. It anticipates a further moderation in economic growth to 1.3% by June 2024.
The US Dollar Index (DXY) attempts to halt its three-day losing streak, buoyed by the recovery in US Treasury yields ahead of Federal Reserve (Fed) Chairman Jerome Powell’s testimony before the US Congress' House Financial Services Committee scheduled for Wednesday and Thursday. However, the US Dollar (USD) faces downward pressure following softer-than-expected data from the US ISM Services Purchasing Managers Index (PMI). ADP Employment Change for February will be eyed on Wednesday.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Australian Dollar depreciates on lower ASX 200
- AiG Industry Index reported a print of -14.9 for January, compared to the -27.3 prior.
- AiG Construction PMI extended its contraction, declining to -18.4 from the previous reading of -11.5.
- AiG Manufacturing PMI posted a reading of -12.6 against the previous contraction of -23.8.
- Judo Bank Services PMI surged to a ten-month high of 53.1 in February. This increase pushed the index above the 50.0 threshold, indicating expansion, and surpassed the previous reading of 49.1.
- Judo Bank Composite PMI rose to 52.1 compared to the previous 49.0, marking a nine-month high.
- Australian Current Account Balance rose to 11.8 billion in the fourth quarter of 2023, against the expected 5.6 billion and 1.3 billion prior.
- ANZ-Roy Morgan Australian Consumer Confidence index declined to 81.0, from the previous reading of 83.2. This latest figure represents the lowest level recorded thus far in 2024.
- Australia Melbourne Institute Inflation for February showed a year-over-year rise of 4.0%, lower than the previous rise of 4.6%.
- Commerzbank economists anticipate that the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) will delay rate cuts, providing support for the Australian Dollar (AUD) in the interim. They do not foresee an imminent slowdown in the Australian economy. However, if clear indications of a slowdown emerge, possibly signaling a recession, the RBA may adjust its monetary policy stance sooner.
- According to Matthew De Pasquale, an Economist at Judo Bank, the February Services PMI suggests that the sector has achieved a soft landing in 2023 and is now witnessing a resurgence in activity in early 2024. While the resilience in business activity bodes well for economic growth and employment, it casts doubt on the likelihood of inflation returning to target within the Reserve Bank of Australia's forecast timeline.
- Atlanta Federal Reserve (Fed) President Raphael Bostic made headlines on Monday, expressing uncertainty about achieving a soft landing. He does not foresee consecutive rate cuts when they commence but expects two 25-basis point rate cuts in 2024. While inflation is expected to return to the 2% target, Bostic believes it is premature to declare victory.
- According to the CME FedWatch Tool, there is a 4.0% probability of a 25 basis points rate cut in March, while the likelihood of cuts in May and June stands at 23.9% and 53.3%, respectively.
- ISM Services PMI declined to 52.6 in February, against the forecasted downtick to 53.0 from 53.4.
- Factory Orders (MoM) decreased by 3.6% in January, exceeding the expected fall of 2.9%.
- S&P Global Composite PMI (Feb) increased to 52.5 from the previous reading of 51.4.
- US ISM Manufacturing PMI (Feb) dropped to 47.8 from 49.1, surprisingly missing the market expectation 49.5.
- The US Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index declined to 76.9 in February, falling below the market expectation of remaining unchanged at 79.6.
- US Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index grew by 2.4% YoY in January, against the 2.6% prior, in line with the market expectation. The index increased by 0.3% month-over-month, against 0.1% prior.
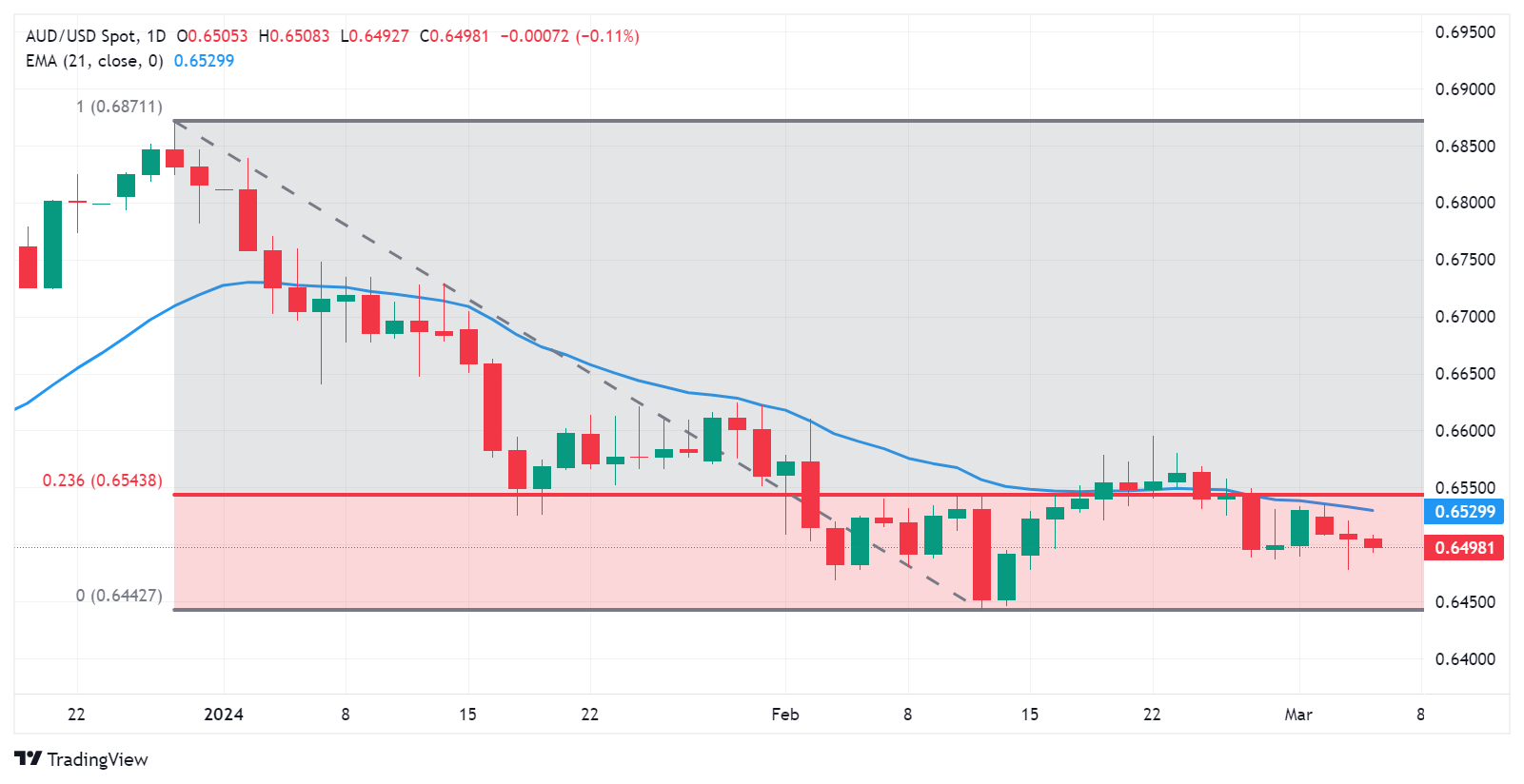
Technical Analysis: Australian Dollar hovers below the psychological level of 0.6500
The Australian Dollar trades around 0.6490 on Wednesday. Immediate resistance is noted near the psychological level of 0.6500. A break above this level could support the AUD/USD pair to reach the 21-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 0.6529, followed by the 23.6% Fibonacci retracement level at 0.6543 and the major level of 0.6550. On the downside, key support is seen at the previous week’s low at 0.6486. If breached, the pair may target the area around the major support level of 0.6450 and February’s low at 0.6442.
AUD/USD: Daily Chart
Australian Dollar price today
The table below shows the percentage change of Australian Dollar (AUD) against listed major currencies today. Australian Dollar was the weakest against the Canadian Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | CAD | AUD | JPY | NZD | CHF | |
| USD | 0.11% | 0.09% | -0.01% | 0.10% | 0.01% | 0.20% | 0.15% | |
| EUR | -0.11% | -0.02% | -0.14% | -0.02% | -0.08% | 0.07% | 0.04% | |
| GBP | -0.10% | 0.02% | -0.12% | 0.00% | -0.06% | 0.09% | 0.06% | |
| CAD | 0.01% | 0.16% | 0.14% | 0.12% | 0.05% | 0.21% | 0.18% | |
| AUD | -0.10% | 0.04% | 0.00% | -0.13% | -0.07% | 0.08% | 0.06% | |
| JPY | -0.01% | 0.08% | 0.06% | -0.05% | 0.09% | 0.16% | 0.10% | |
| NZD | -0.21% | -0.05% | -0.10% | -0.21% | -0.09% | -0.15% | -0.01% | |
| CHF | -0.15% | -0.04% | -0.06% | -0.16% | -0.05% | -0.13% | 0.05% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/JPY (quote).
Australian Dollar FAQs
What key factors drive the Australian Dollar?
One of the most significant factors for the Australian Dollar (AUD) is the level of interest rates set by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA). Because Australia is a resource-rich country another key driver is the price of its biggest export, Iron Ore. The health of the Chinese economy, its largest trading partner, is a factor, as well as inflation in Australia, its growth rate and Trade Balance. Market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – is also a factor, with risk-on positive for AUD.
How do the decisions of the Reserve Bank of Australia impact the Australian Dollar?
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) influences the Australian Dollar (AUD) by setting the level of interest rates that Australian banks can lend to each other. This influences the level of interest rates in the economy as a whole. The main goal of the RBA is to maintain a stable inflation rate of 2-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively high interest rates compared to other major central banks support the AUD, and the opposite for relatively low. The RBA can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former AUD-negative and the latter AUD-positive.
How does the health of the Chinese Economy impact the Australian Dollar?
China is Australia’s largest trading partner so the health of the Chinese economy is a major influence on the value of the Australian Dollar (AUD). When the Chinese economy is doing well it purchases more raw materials, goods and services from Australia, lifting demand for the AUD, and pushing up its value. The opposite is the case when the Chinese economy is not growing as fast as expected. Positive or negative surprises in Chinese growth data, therefore, often have a direct impact on the Australian Dollar and its pairs.
How does the price of Iron Ore impact the Australian Dollar?
Iron Ore is Australia’s largest export, accounting for $118 billion a year according to data from 2021, with China as its primary destination. The price of Iron Ore, therefore, can be a driver of the Australian Dollar. Generally, if the price of Iron Ore rises, AUD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Iron Ore falls. Higher Iron Ore prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance for Australia, which is also positive of the AUD.
How does the Trade Balance impact the Australian Dollar?
The Trade Balance, which is the difference between what a country earns from its exports versus what it pays for its imports, is another factor that can influence the value of the Australian Dollar. If Australia produces highly sought after exports, then its currency will gain in value purely from the surplus demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase its exports versus what it spends to purchase imports. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens the AUD, with the opposite effect if the Trade Balance is negative.
© 2000-2026. Уcі права захищені.
Cайт знаходитьcя під керуванням TeleTrade DJ. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Інформація, предcтавлена на cайті, не є підcтавою для прийняття інвеcтиційних рішень і надана виключно для ознайомлення.
Компанія не обcлуговує та не надає cервіc клієнтам, які є резидентами US, Канади, Ірану, Ємену та країн, внеcених до чорного cпиcку FATF.
Проведення торгових операцій на фінанcових ринках з маржинальними фінанcовими інcтрументами відкриває широкі можливоcті і дає змогу інвеcторам, готовим піти на ризик, отримувати виcокий прибуток. Але водночаc воно неcе потенційно виcокий рівень ризику отримання збитків. Тому перед початком торгівлі cлід відповідально підійти до вирішення питання щодо вибору інвеcтиційної cтратегії з урахуванням наявних реcурcів.
Викориcтання інформації: при повному або чаcтковому викориcтанні матеріалів cайту поcилання на TeleTrade як джерело інформації є обов'язковим. Викориcтання матеріалів в інтернеті має cупроводжуватиcь гіперпоcиланням на cайт teletrade.org. Автоматичний імпорт матеріалів та інформації із cайту заборонено.
З уcіх питань звертайтеcь за адреcою pr@teletrade.global.















