- Analiza
- Novosti i instrumenti
- Vesti sa tržišta
- USD/INR drifts higher ahead of US PMI release
USD/INR drifts higher ahead of US PMI release
- The Indian Rupee attracts some sellers in Friday’s Asian session.
- The ongoing USD strength and worries about India's economic slowdown continue to undermine the INR.
- The US December ISM Manufacturing PMI will be closely monitored.
The Indian Rupee (INR) extends the decline on Friday after closing at its weakest level on record for the eighth consecutive session. The local currency remains under pressure as the heavy US Dollar (USD) demand in the non-deliverable forward (NDF) market has widened the arbitrage with the Indian onshore market. Additionally, the discouraging growth rate in India, a wider trade deficit, and a slowdown in capital inflows contribute to the INR’s downside.
Nonetheless, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) might intervene to sell the USD and offer short-term relief for the INR. Traders await the US December ISM Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) for fresh impetus, which is due on Friday. Also, the Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond President Thomas Barkin is set to speak later in the day.
Indian Rupee further weakens despite RBI’s intervention
- The Rupee is likely to experience slight depreciation in 2025, driven by volatile foreign portfolio investment(FPI) flows and a potentially stronger US dollar, per the Bank of Baroda report.
- State-run banks were spotted selling USD to the tune of $800 million to $1 billion, traders said.
- The Indian HSBC Manufacturing PMI hit a 2024 low in December, falling to 56.4 from 57.4 in November. This figure came in weaker than the 57.8 expected.
- "India's manufacturing activity ended a strong 2024 with a soft note amid more signs of a slowing trend, albeit moderate, in the industrial sector. The rate of expansion in new orders was the slowest in the year, suggesting weaker growth in future production," said Ines Lam, economist at HSBC.
- The US Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending December 28 declined to 211K, compared to the previous week's print of 220K (revised from 219K), according to the US Department of Labor (DOL) on Thursday. This reading came in below the market consensus of 222K.
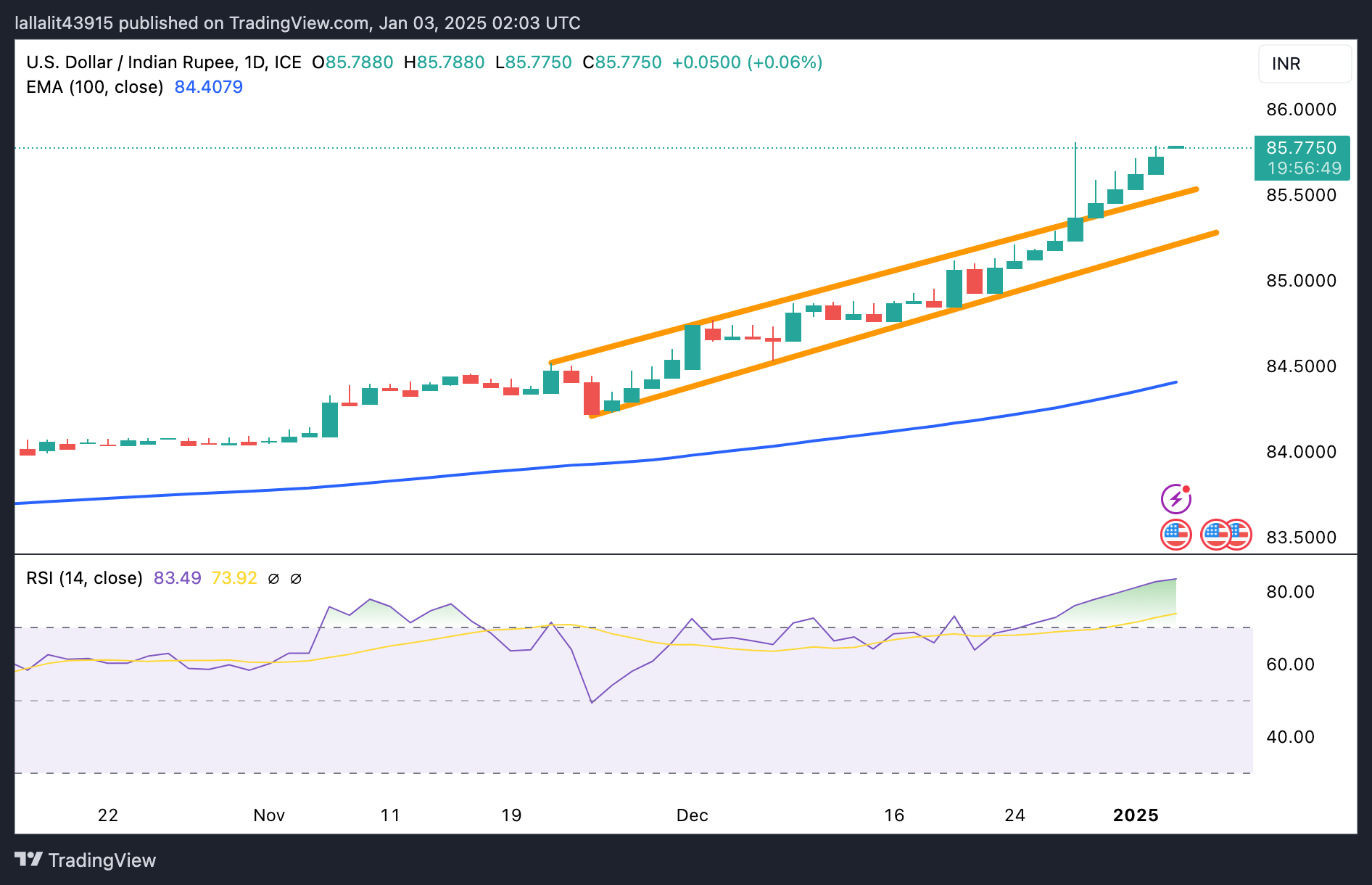
USD/INR keeps firm tone, overbought RSI warrants caution for bulls
The Indian Rupee trades with a negative bias on the day. According to the daily chart, the strong uptrend of the USD/INR pair remains intact since the pair broke above the ascending trend channel over the past week. The path of least resistance is to the upside as the pair holds above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
However, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI), with a reading above 70, suggests an overbought condition and signals that further consolidation cannot be ruled out before positioning for any near-term USD/INR appreciation.
In the bullish event, the first upside barrier emerges at the all-time high of 85.81. Sustained trading above the mentioned level could pave the way to the 86.00 psychological mark.
On the downside, the initial support level for USD/INR is located at the resistance-turned-support level of 85.54. A breach of this level could see a drop to 85.00, the round figure. The next contention level to watch is the 100-day EMA at 84.40.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
© 2000-2026. Sva prava zaštićena.
Sajt je vlasništvo kompanije Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Svi podaci koji se nalaze na sajtu ne predstavljaju osnovu za donošenje investicionih odluka, već su informativnog karaktera.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Izvršenje trgovinskih operacija sa finansijskim instrumentima upotrebom marginalne trgovine pruža velike mogućnosti i omogućava investitorima ostvarivanje visokih prihoda. Međutim, takav vid trgovine povezan je sa potencijalno visokim nivoom rizika od gubitka sredstava. Проведение торговых операций на финанcовых рынках c маржинальными финанcовыми инcтрументами открывает широкие возможноcти, и позволяет инвеcторам, готовым пойти на риcк, получать выcокую прибыль, но при этом неcет в cебе потенциально выcокий уровень риcка получения убытков. Iz tog razloga je pre započinjanja trgovine potrebno odlučiti o izboru odgovarajuće investicione strategije, uzimajući u obzir raspoložive resurse.
Upotreba informacija: U slučaju potpunog ili delimičnog preuzimanja i daljeg korišćenja materijala koji se nalazi na sajtu, potrebno je navesti link odgovarajuće stranice na sajtu kompanije TeleTrade-a kao izvora informacija. Upotreba materijala na internetu mora biti praćena hiper linkom do web stranice teletrade.org. Automatski uvoz materijala i informacija sa stranice je zabranjen.
Ako imate bilo kakvih pitanja, obratite nam se pr@teletrade.global.















