- Analiza
- Novosti i instrumenti
- Vesti sa tržišta
- USD/INR remains confined within a narrow range, 16th BRICS Summit reaches its final day
USD/INR remains confined within a narrow range, 16th BRICS Summit reaches its final day
- The Indian Rupee trades within a tight range of 84.00-84.10.
- Indian PM Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping agreed to enhance communication and cooperation during the BRICS summit on Wednesday.
- Traders are likely to observe India’s HSBC Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) data on Thursday.
The Indian Rupee (INR) steadies against the US Dollar (USD) on Thursday, with the USD/INR pair hovering within the 84.00-84.10 range. Market interventions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) helped limit downside risks for the INR, despite continued outflows from Indian equities.
The Rupee received downward pressure as Foreign Institutional Investors (FII) were net sellers of Indian stocks for the 18th consecutive session on Wednesday, shifting funds to China due to stimulus measures and more attractive valuations. The Nifty 50 has fallen 1.7% over the past three sessions this week and is down about 6% from last week's record highs, weighed down by disappointing earnings results.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping held their first formal talks in five years on the sidelines of the BRICS summit in Russia. During their meeting on Wednesday, the two leaders agreed to enhance communication and cooperation between India and China, aiming to resolve ongoing conflicts and improve relations that were strained following a deadly military clash in 2020, according to Reuters.
Traders are likely to keep an eye on the HSBC Purchasing Managers Index (PMI), a key indicator of business activity in India, which is set to be released on Thursday. Attention will also turn to FX Reserves (USD) data for the week ending October 14, expected to be published on Friday.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Indian Rupee resists downward pressure due to potential RBI intervention
- The US Dollar faced downward pressure following the release of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) Beige Book on Wednesday. The latest report indicated that economic activity was "little changed in nearly all Districts," in contrast to August's report, where three Districts reported growth and nine showed flat activity.
- According to the CME FedWatch Tool, there is an 88.9% probability of a 25-basis-point rate cut, with no expectation of a larger 50-basis-point cut.
- Jim O'Neill, the former Goldman Sachs economist who coined the term BRIC in 2001, told Reuters that the notion of the BRICS group challenging the US Dollar is unrealistic as long as China and India remain divided and unwilling to cooperate on trade.
- In the minutes from the October meeting, members of the rate-setting panel stated that the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) must take a cautious approach to lowering interest rates, as India cannot afford to face another bout of inflation.
- In a speech at the New York Fed Central Banking Seminar, RBI Deputy Governor Michael Patra stated, "We believe that the best defense against global risks is to strengthen the macroeconomic fundamentals and build adequate buffers, supported by prudent macroeconomic policies." He highlighted that India’s central bank has been strategically increasing its foreign exchange reserves, which are now equivalent to or nearly equal to 12 months' worth of imports.
- In a post on the social media platform X, Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco President Mary Daly stated that the economy is clearly in a better position, with inflation having fallen significantly and the labor market returning to a more sustainable path.
- Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis President Neel Kashkari highlighted on Monday that the Fed is closely monitoring the US labor market for signs of rapid destabilization. Kashkari cautioned investors to anticipate a gradual pace of rate cuts over the coming quarters, suggesting that any monetary easing will likely be moderate rather than aggressive.
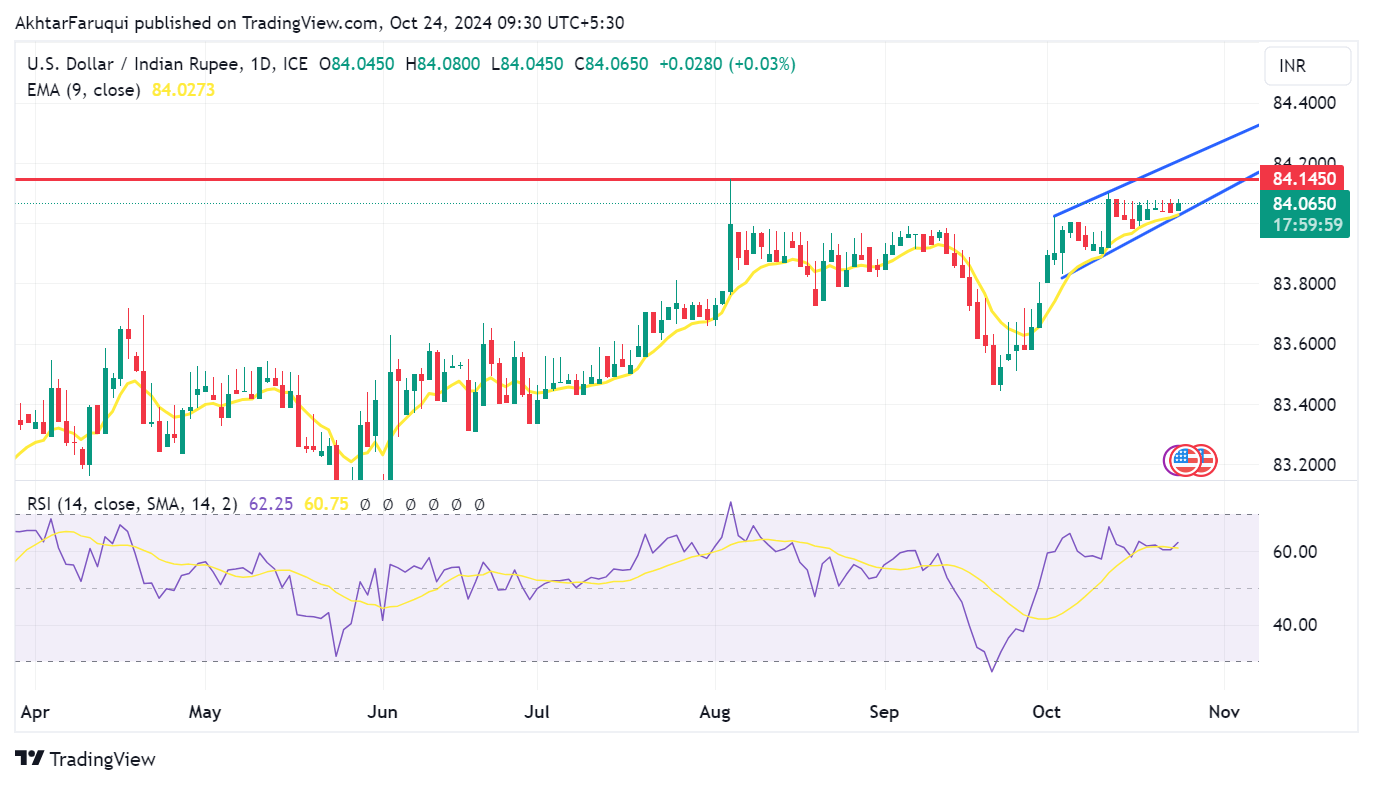
Technical Analysis: USD/INR finds support around 84.00, nine-day EMA
The USD/INR pair holds steady above 84.00 on Thursday. An analysis of the daily chart shows that the pair is hovering within an ascending channel pattern, suggesting a bullish bias. The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is nearing the 70 mark, which further reinforces the current bullish momentum.
In terms of resistance, the pair may face obstacles at its all-time high of 84.14, reached on August 5. A breakout above this level could enable the USD/INR pair to test the upper boundary of the ascending channel, which is around 84.20.
On the support side, immediate backing is located at the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near the 84.02 level, coinciding with the lower boundary of the ascending channel and the psychological level of 84.00.
USD/INR: Daily Chart
US Dollar PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of US Dollar (USD) against listed major currencies today. US Dollar was the strongest against the Swiss Franc.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.09% | -0.04% | -0.32% | -0.08% | -0.20% | -0.16% | -0.04% | |
| EUR | 0.09% | 0.03% | -0.25% | 0.00% | -0.13% | -0.09% | 0.02% | |
| GBP | 0.04% | -0.03% | -0.28% | -0.04% | -0.17% | -0.13% | -0.00% | |
| JPY | 0.32% | 0.25% | 0.28% | 0.25% | 0.12% | 0.13% | 0.28% | |
| CAD | 0.08% | -0.00% | 0.04% | -0.25% | -0.11% | -0.08% | 0.03% | |
| AUD | 0.20% | 0.13% | 0.17% | -0.12% | 0.11% | 0.05% | 0.16% | |
| NZD | 0.16% | 0.09% | 0.13% | -0.13% | 0.08% | -0.05% | 0.12% | |
| CHF | 0.04% | -0.02% | 0.00% | -0.28% | -0.03% | -0.16% | -0.12% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the US Dollar from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent USD (base)/JPY (quote).
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
© 2000-2026. Sva prava zaštićena.
Sajt je vlasništvo kompanije Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
Svi podaci koji se nalaze na sajtu ne predstavljaju osnovu za donošenje investicionih odluka, već su informativnog karaktera.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Izvršenje trgovinskih operacija sa finansijskim instrumentima upotrebom marginalne trgovine pruža velike mogućnosti i omogućava investitorima ostvarivanje visokih prihoda. Međutim, takav vid trgovine povezan je sa potencijalno visokim nivoom rizika od gubitka sredstava. Проведение торговых операций на финанcовых рынках c маржинальными финанcовыми инcтрументами открывает широкие возможноcти, и позволяет инвеcторам, готовым пойти на риcк, получать выcокую прибыль, но при этом неcет в cебе потенциально выcокий уровень риcка получения убытков. Iz tog razloga je pre započinjanja trgovine potrebno odlučiti o izboru odgovarajuće investicione strategije, uzimajući u obzir raspoložive resurse.
Upotreba informacija: U slučaju potpunog ili delimičnog preuzimanja i daljeg korišćenja materijala koji se nalazi na sajtu, potrebno je navesti link odgovarajuće stranice na sajtu kompanije TeleTrade-a kao izvora informacija. Upotreba materijala na internetu mora biti praćena hiper linkom do web stranice teletrade.org. Automatski uvoz materijala i informacija sa stranice je zabranjen.
Ako imate bilo kakvih pitanja, obratite nam se pr@teletrade.global.