- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- USD/INR trades flat as traders await US Retail Sales release
USD/INR trades flat as traders await US Retail Sales release
- The Indian Rupee flat lines in Tuesday’s Asian session.
- Rising US bond yields and a weaker Chinese Yuan could undermine the INR, but the RBI’s intervention might help limit its losses.
- Traders brace for the US November Retail Sales on Tuesday ahead of the Fed rate decision.
The Indian Rupee (INR) consolidates in a narrow trading range on Tuesday after weakening to a new closing low in the previous session. A rise in US Treasury bond yields and weakness in the Chinese Yuan exert some selling pressure on the local currency. Furthermore, the widening of India’s merchandise trade deficit in November further weighs on the INR.
Any significant depreciation of the Indian Rupee might be limited as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will likely sell the USD via state-owned banks to avoid excess volatility. The US November Retail Sales is due later on Tuesday. All eyes will be on the US Federal Reserve (Fed) interest rate decision on Wednesday for fresh catalysts. Also, the Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s press conference and the updated economic projections will be closely monitored.
Indian Rupee holds steady on the back of global cues
- The Indian WPI inflation eased to a three-month low of 1.89% in November from 2.36% in October, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry showed on Monday. This figure came in softer than the expectation of 2.2%.
- The preliminary estimate released by HSBC showed on Monday that the India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) rose to 57.4 in December versus 56.5 prior.
- The Indian Services PMI climbed to 60.8 in December from 58.4 prior. The Composite PMI jumped to 60.7 during the same report period from 58.6 in November.
- "The small rise in the headline manufacturing PMI in December was mainly driven by gains in current production, new orders, and employment," said Ines Lam, economist at HSBC.
- The US S&P Global Composite PMI improved to 56.6 in December’s flash estimate versus 54.9 prior. Meanwhile, the Services PMI increased to 58.5 in December’s flash estimate from 56.1. The Manufacturing PMI eased to 48.3 from 49.7.
USD/INR keeps the bullish vibe in the longer term
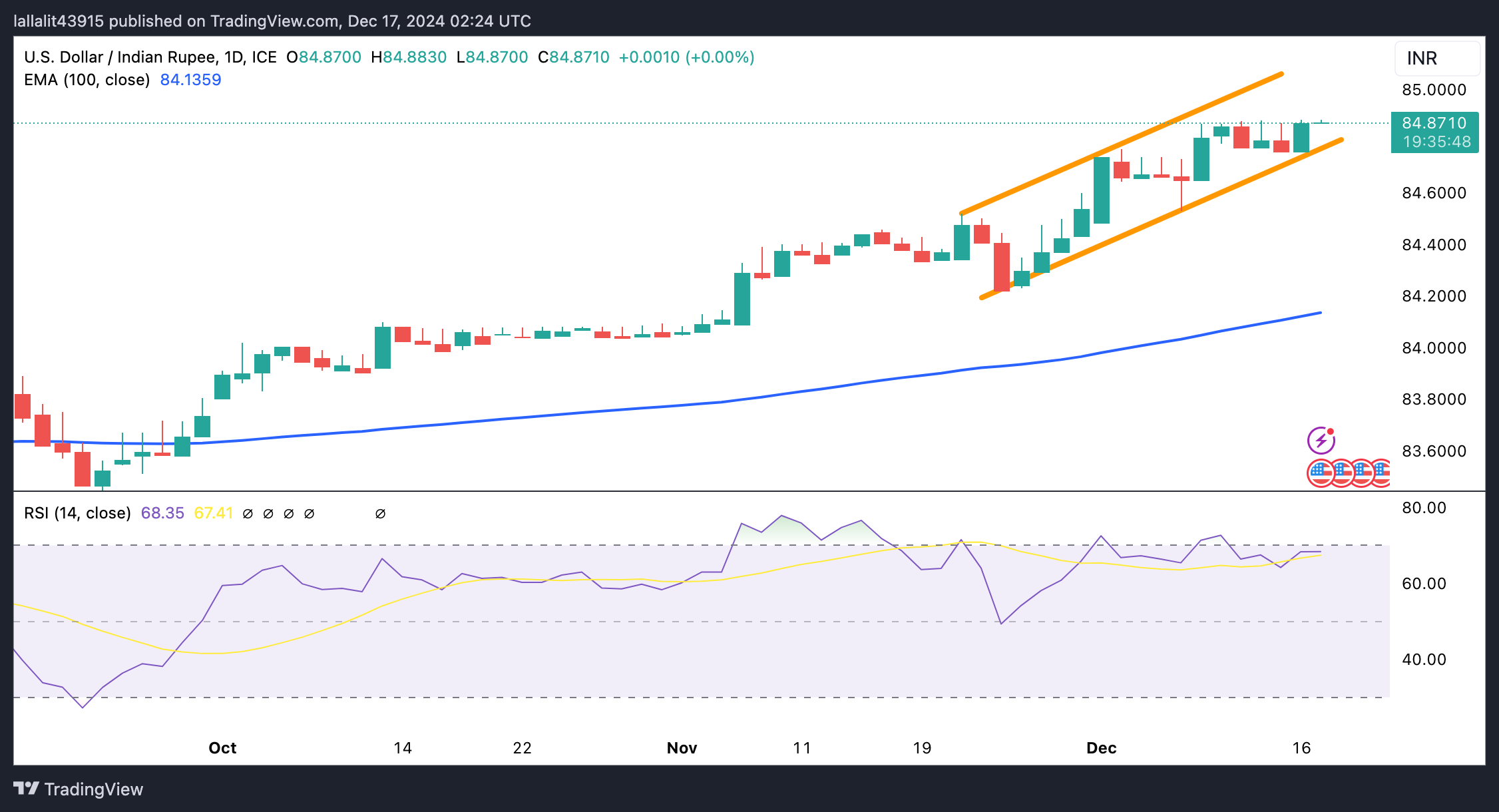
The Indian Rupee trades flat on the day. The constructive view of the USD/INR pair prevails, with the price holding above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) on the daily chart. Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is located above the midline near 68.35, supporting the buyers in the near term.
The ascending trend channel and the psychological level of 85.00 appear to be a tough nut to crack for bulls. Sustained bullish momentum could even take USD/INR to 85.50.
On the other hand, the first downside target to watch is the lower boundary of the trend channel of 84.80. A breach of this level could expose 84.22, the low of November 25. The potential support level for the pair is seen at 84.13, the 100-day EMA.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.