- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- US Dollar soars to four-month high as Trump wins US presidency
US Dollar soars to four-month high as Trump wins US presidency
- The US Dollar is firmly in the green, with more than one-percentage-point gain against most major peers.
- Former US President Donald Trump has secured the 270 electoral votes needed to become the next US president.
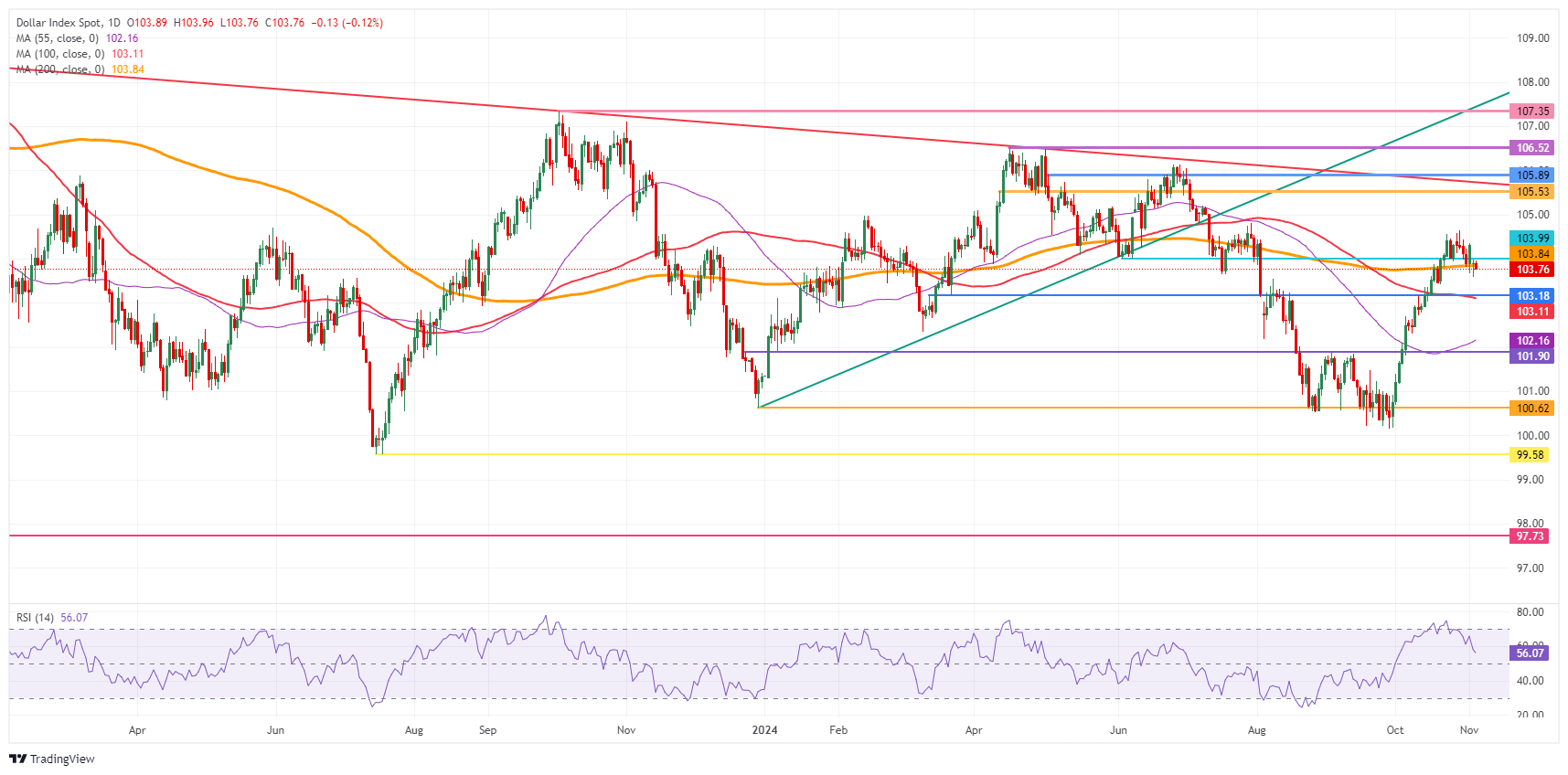
- The US Dollar index broke above 105.00, the highest level since July, and retreated slightly afterward.
The US Dollar (USD) rises sharply on Wednesday after former US President Donald Trump secured enough electoral votes to become the next US president. The former US President has secured 277 votes, more than enough to surpass the magic 270 threshold needed to secure a majority. An additional element that might result in more US Dollar strength is the fact that the Republicans have secured a majority in the Senate. While the race to control the US House of Representatives is still undecided, it looks like Trump will not be a lame-duck president and will have support from both institutions when it comes to passing laws.
The US economic calendar is very light on Wednesday. It looks like traders will be able to further assess and focus on the outcome of the US presidential election. Besides the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) weekly Mortgage Application numbers, nothing special is expected on the economic data front.
Daily digest market movers: Trump has been elected as US president
- At the time of writing, former US President Donald Trump has secured 277 electoral votes and has comfortably reached the 270 threshold to win. Vice President Kamala Harris is lagging behind with only 224.
- Asian equities saw China being hurt, with tariffs underway once Trump is sworn in next year. European and US equities are rallying higher.
- The CME FedWatch Tool is backing a 25 basis point (bps) interest-rate cut by the Federal Reserve (Fed) on Thursday’s meeting with a 97.5% probability. More interesting is the December 18 meeting, where a 50 bps interest-rate cut from the current level is expected by a 68.4% chance, suggesting that markets anticipate a rate cut this week and in December. Before the US election outcome, the probability was still at 80%.
- The US 10-year benchmark rate trades at 4.35%, settling down a bit after hitting 4.46% earlier.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Hail to the King!
The US Dollar Index (DXY) is reclaiming its throne as the King of all currencies. The Greenback has been gaining in several big figures against most of the major G20 currencies, resulting in a US Dollar Index that broke above the 105.00 level. With a small fade taking place at the moment, looking for near support will be vital, while markets will need to wait for a few months until Donald Trump is sworn in again as President and starts to take measures, introduce tariffs, and other elements that will move all asset classes.
The new levels to look out for on the upside are not seen since June and July. The first up is 105.53 (April 11 high), a very firm cap resistance, with 105.89 (May 2 high) just above. Once that is broken, 106.52, the high of April and a double top, will be the last level standing before starting to talk about 107.00.
On the downside, last week’s peak at 104.63 looks to be the first pivotal support nearby. Should the fade become bigger, the round level of 104.00 and the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 103.85 should refrain from sending the DXY any lower.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.