- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- Pound Sterling tumbles on soft UK inflation
Pound Sterling tumbles on soft UK inflation
- The Pound Sterling falls vertically after the UK inflation data for September came in slower than expected.
- UK annual headline CPI decelerated below the bank’s target of 2%.
- Traders expect the Fed to cut interest rates moderately in the remainder of the year.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) faces an intense sell-off as the United Kingdom (UK) Office for National Statistics (ONS) has published a soft Consumer Price Index (CPI) report for September. The CPI report showed that the annual headline inflation softened to 1.7%. Price pressures were expected to decelerate but at a slower pace to 1.9% from 2.2% in August. Month-on-month headline inflation remained flat.
The core CPI inflation – which excludes volatile items such as food, energy, oil, and tobacco – decelerated at a faster-than-expected pace to 3.2%, from the estimates of 3.4% and the former reading of 3.6%. Services inflation, a closely watched indicator by Bank of England (BoE) officials, grew at a slower pace of 4.9% from 5.6% in August. A sharp deceleration in price pressures is expected to force traders to raise bets supporting interest rate cuts in each of the two policy meetings remaining this year.
Currently, financial market participants expect the BoE to cut interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) in one of the policy meetings scheduled in November and December.
Market experts were anticipating a slowdown in the service inflation as growth in the UK’s Average Earnings Excluding Bonuses, a wage growth measure that drives consumer spending, in the three months ending August was the slowest in two years. The wage growth measure rose expectedly by 4.9%, slower than the prior release of 5.1%.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling weakens against US Dollar
- The Pound Sterling falls vertically below the psychological support of 1.3000 against the US Dollar (USD) in Wednesday’s London session. The US Dollar stays afloat near a more than two-month high as traders have priced in moderate interest rate cuts from the Federal Reserve (Fed) in the remaining policy meetings this year, with the US Dollar Index (DXY) holding onto gains near 103.30. The Fed started the policy-easing cycle with a larger-than-usual size of 50 basis points (bps) in September.
- According to the CME FedWatch tool, 30-day Federal Funds futures pricing data suggests that there will be interest rate cuts by 25 bps in the November and December meetings.
- Traders have priced out expectations of another 50 bps rate cut in November after a string of better-than-expected United States (US) data for September, which showed signs of economic resilience. US data such as Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) and the ISM Services PMI grew at a robust pace, diminishing fears of an economic slowdown.
- Apart from the upbeat US data, price pressures grew at a faster-than-expected pace in September, signaling that the battle against inflation is far from over.
- Going forward, investors will pay close attention to the monthly US Retail Sales data for September, which will be published on Thursday. The Retail Sales data, a key measure of consumer spending, is estimated to have grown by 0.3%.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling tests region below 1.3000
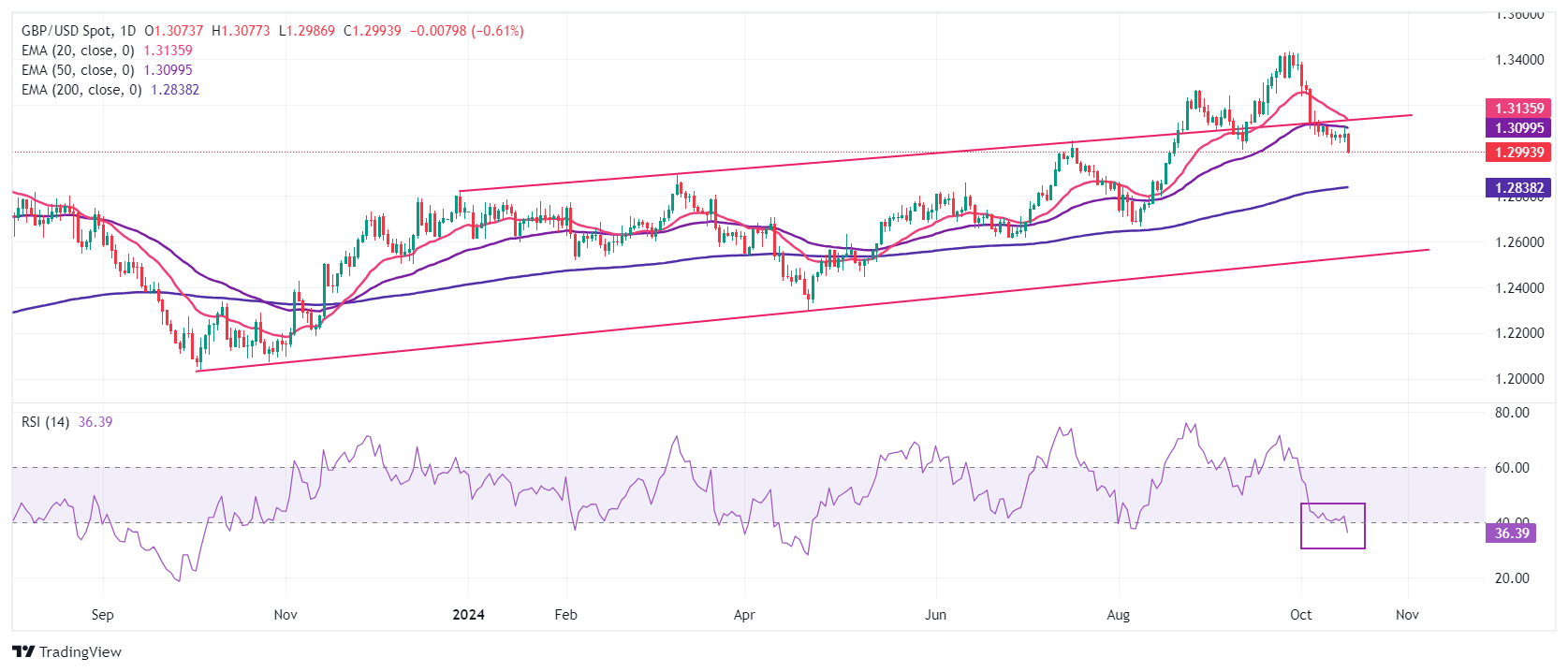
The Pound Sterling slides below 1.3000 against the US Dollar in European trading hours. The GBP/USD pair weakens after breaking below the four-day trading range of 1.3020-1.3100. The Cable was already under pressure after slipping below the upward-sloping trendline plotted from the 28 December 2023 high of 1.2827 earlier in October.
The near-term trend of the major appears to be vulnerable as the 20- and 50-day Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs) near 1.3135 and 1.3100, respectively, are sloping downwards.
A downside move in the Relative Strength Index (RSI) below 40.00 suggests a bearish momentum.
Looking down, the 200-day EMA near 1.2840 will be a major support zone for Pound Sterling bulls. On the upside, the Cable will face resistance near the round-level figure of 1.3100.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.