- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- USD/INR remains stronger as traders evaluate RBI’s policy outlook following inflation data
USD/INR remains stronger as traders evaluate RBI’s policy outlook following inflation data
- The Indian Rupee faces challenges due to foreign exchange outflows.
- India’s annual inflation rose to a nine-month high of 5.49% in September, dampening the likelihood of RBI’s rate cuts.
- The downside of the INR could be restrained due to falling Oil prices, as India is world's third-largest Oil importer.
The USD/INR pair remains near its all-time high at 84.14 as the Indian Rupee (INR) grapples with challenges stemming from foreign exchange outflows. This situation arises as traders evaluate the policy outlook for the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in light of the recent inflation data from India.
India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose to a nine-month high of 5.49% year-over-year in September, up from 3.65% in the previous month and well above market expectations of 5.0%. This increase represents the highest inflation rate recorded this year, surpassing the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) target of 4%. As a result, expectations for earlier rate cuts by the RBI have been tempered.
The Indian Rupee may receive support from falling Oil prices, given that India is the world's third-largest Oil importer. Crude Oil prices are facing downward pressure due to concerns about global demand, which have outweighed the impact of supply worries related to the ongoing uncertainty in the Middle East conflict.
West Texas Intermediate (WTI) Oil price extends its losing streak for the fourth successive session, trading around $70.30 per barrel, at the time of writing.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Indian Rupee struggles due to foreign exchange outflows
- The US Dollar (USD) continues to strengthen, bolstered by strong employment and Consumer Price Index (CPI) data that have lowered expectations for aggressive easing by the Federal Reserve (Fed). Markets are now projecting a total of 125 basis points in rate cuts over the next 12 months.
- According to the CME FedWatch Tool, there is currently a 94.1% probability of a 25-basis-point rate cut in November, with no expectation of a larger 50-basis-point reduction.
- On Tuesday, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta President Raphael Bostic stated that he anticipates just one more interest rate cut of 25 basis points this year, as reflected in his projections during last month's US central bank meeting. "The median forecast was for 50 basis points beyond the 50 basis points already implemented in September, according to Reuters.
- On Monday, Foreign institutional investors sold a net total of 37.32 billion rupees ($444 million) in stocks, marking their eleventh consecutive session of net selling. In contrast, domestic investors net purchased shares valued at 22.78 billion rupees, per Reuters.
- The Washington Post reported on Monday that Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu informed the United States (US) that Israel plans to focus on Iranian military targets rather than nuclear or Oil infrastructure.
- Federal Reserve (Fed) Bank of Minneapolis President Neel Kashkari reassured markets late on Monday by reaffirming the Fed's data-dependent approach. Kashkari reiterated familiar Fed policymaker views on the strength of the US economy, noting continued easing of inflationary pressures and a robust labor market, despite a recent uptick in the overall unemployment rate, per Reuters.
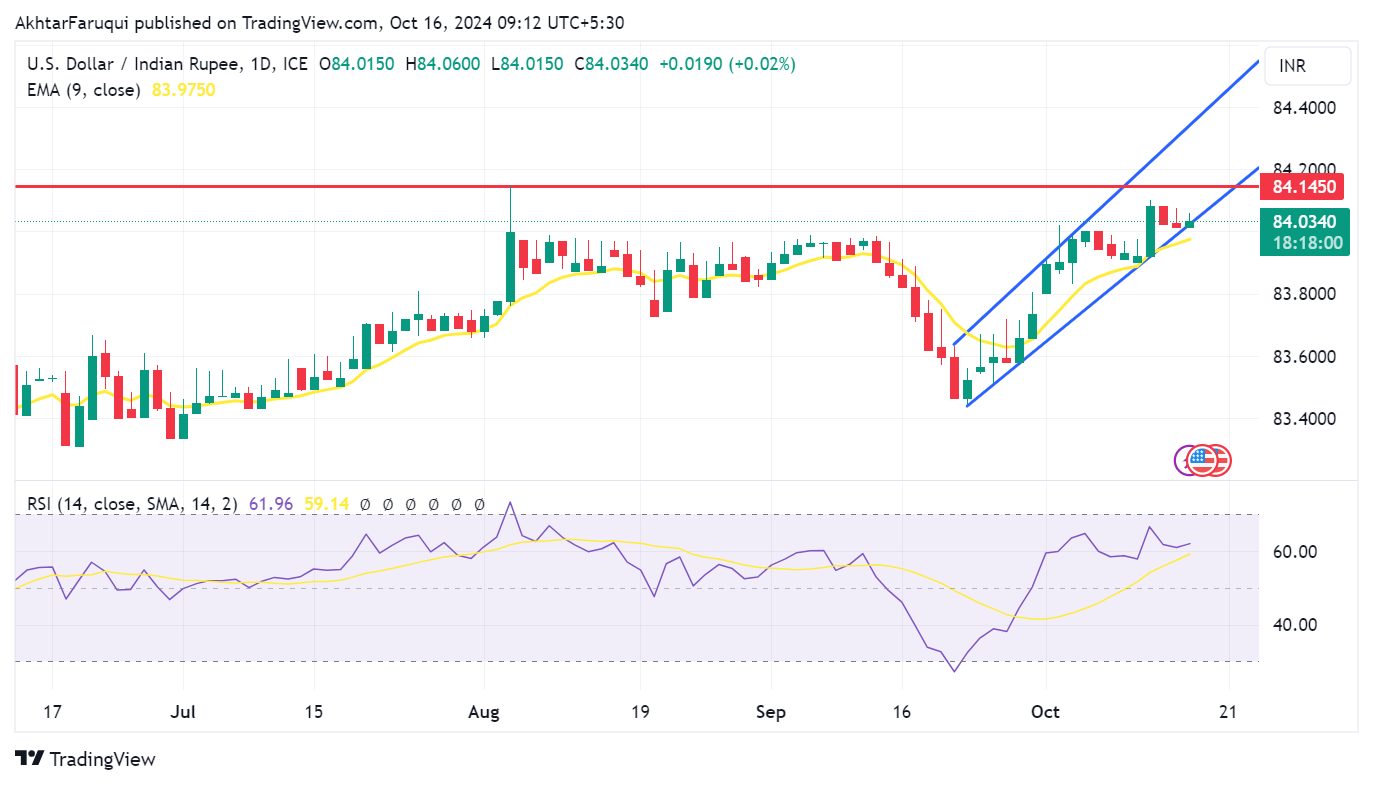
Technical Analysis: USD/INR holds position above 84.00, close to all-time highs
The USD/INR pair hovers around 84.00 on Wednesday. Analyzing the daily chart shows that the pair is testing the lower boundary of an ascending channel pattern. If it breaks below this channel, it could indicate a potential shift away from the current bullish sentiment. However, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) remains above the 50 level, which suggests that bullish momentum is still intact.
In terms of resistance, the USD/INR pair may encounter a barrier at its all-time high of 84.14, recorded on August 5. A breakthrough above this level could push the pair toward the upper boundary of the ascending channel, estimated at around 84.35.
On the downside, if the pair breaks below the immediate support at the psychological level of 84.00, it may target the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at approximately 83.97.
USD/INR: Daily Chart
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.