- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- Canadian Dollar falls further as Canadian Trade Balance contracts
Canadian Dollar falls further as Canadian Trade Balance contracts
- The Canadian Dollar lost another quarter percent on Tuesday.
- Canada saw a steeper-than-expected contraction in trade balance figures.
- Fed Meeting Minutes to reveal further details about Fed’s latest rate moves.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) shed another quarter of a percent against the Greenback on Tuesday, trimming lower slipping back against the US Dollar for a fifth straight trading day. The CAD has shed almost 2% against the Greenback since peaking in late September.
Canada’s trade balance contracted more than expected in August, with Exports falling and Imports clocking in only a minor upswing. US trade balance figures moderated, and Fedspeak continues to dominate market flows as investors look for signs of more rate cuts.
Daily digest market movers
- The CAD shed weight on Tuesday, contracting another 0.25% against the Greenback.
- Canadian International Merchandise Trade in August fell $1.1 billion, much steeper than the forecast $-500 million.
- The decline in Canadian Merchandise Trade was sparked by a deeper cut to Exports, which fell from $65.66 billion to $64.31 billion compared to a softer rise in Imports, to $65.41 billion from $64.97 billion.
- Fed’s latest Meeting Minutes set to release on Wednesday as Fedspeak continues to chill rate cut hopes.
- Read more:
Fed's Collins: US economy, labor market remain strong
Fed's Bostic: Jobs market is not weak, economy might be too strong for policy recalibration
Canadian Dollar price forecast
The USD/CAD daily chart shows a clear upward momentum that has developed in recent trading sessions. The price has moved above both the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 1.35880 and the 200-day EMA at 1.36048, which often signals a potential trend shift or the continuation of a bullish trend. Breaking these key moving averages is a significant technical indicator suggesting that bullish sentiment is building in the market. The price is now hovering around 1.36515, a level that could act as a short-term resistance point.
The MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) at the bottom of the chart is currently displaying a bullish crossover. The MACD line (blue) has crossed above the signal line (orange), which is a positive sign for further upward momentum. Additionally, the histogram bars have shifted into positive territory, confirming that bullish pressure is increasing. This could indicate that the market is gaining momentum and further upside is possible if these signals remain intact.
However, caution should be exercised as the price is approaching potential resistance areas just above the current levels, which could prompt some profit-taking. If the price fails to break decisively above the recent high, it may consolidate around the EMAs or retrace back to test support levels at the 1.35880 or 1.36048 areas. Overall, the technical outlook for USD/CAD is currently bullish, but traders should watch for signs of exhaustion or a breakout above current resistance for confirmation of further gains.
USD/CAD daily chart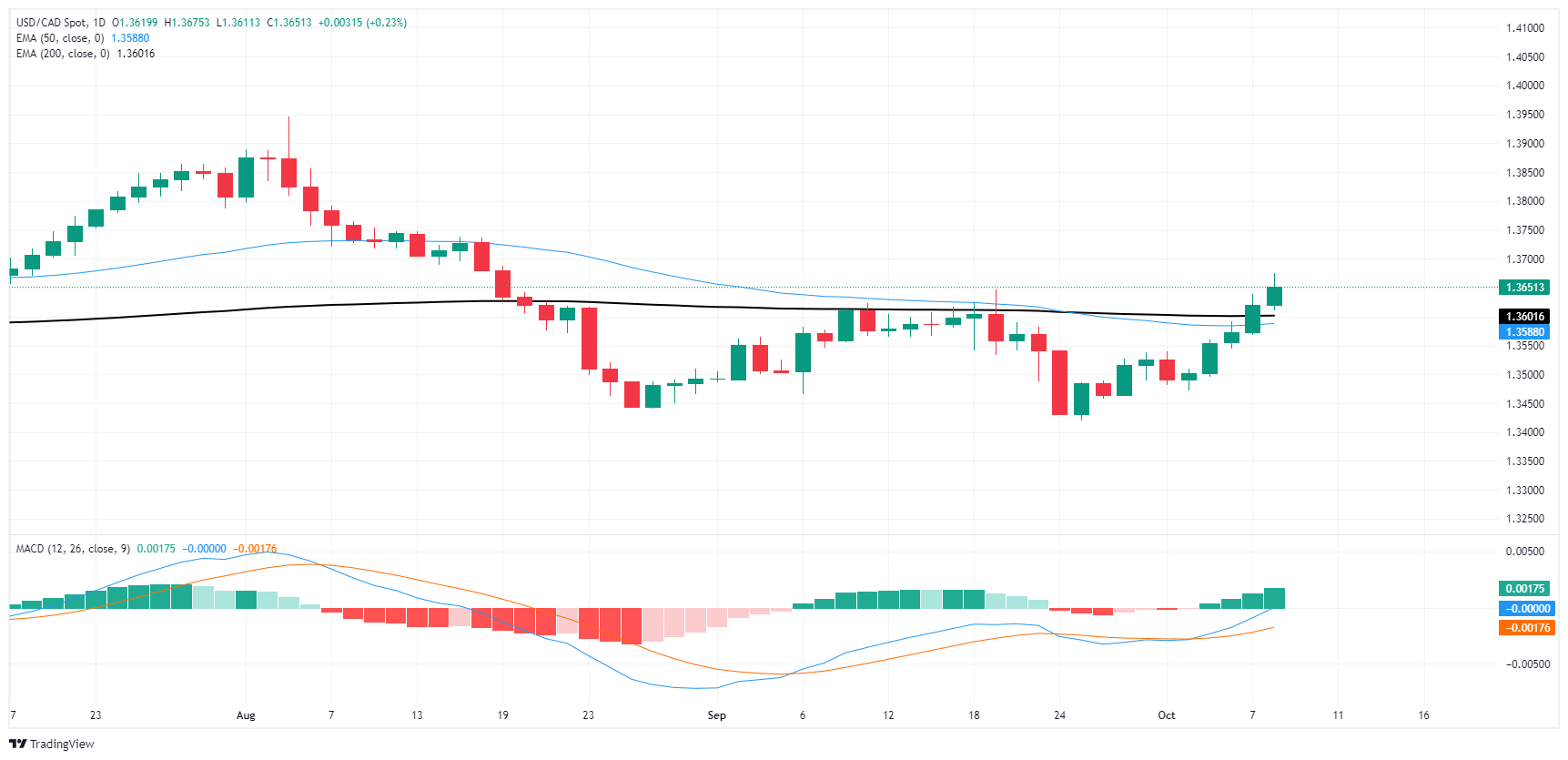
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.















