- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- USD/INR edges lower ahead of Fed Chair Powell’s speech
USD/INR edges lower ahead of Fed Chair Powell’s speech
- The Indian Rupee strengthens in Friday’s Asian session.
- Fed's dovish remarks, decline of crude oil prices and RBI intervention continue to underpin the INR.
- Investors will closely monitor Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s speech on Friday.
The Indian Rupee (INR) trades with mild gains on Friday as the dovish US Federal Reserve (Fed) minutes and lower crude oil prices support the local currency. Traders also expect the INR’s downside might be limited as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) might step in to sell the USD and prevent the INR from breaching the key 84.00 level.
Nonetheless, the relentless Greenback demand from importers and ongoing foreign fund outflows might dampen investor sentiments and drag the Indian Rupee lower. The Fed Chair Jerome Powell's speech at the Jackson Hole Symposium will take center stage on Friday, which could offer some insight into the future US interest rate path.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Indian Rupee rebounds, but potential upside seems limited
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released the minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting on Thursday, highlighting that the policy must continue to be actively disinflationary to ensure anchoring of inflation to its target level.
- The Indian central bank noted that headline inflation has seen upward movement in June to 5.1% as food inflation pressures increased and offset the impact of subdued core inflation and deflation in the fuel group.
- The preliminary HSBC India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) declined to 57.9 in August from 58.1 in July. Services PMI rose to 60.4 in August from the previous reading of 60.3.
- The US S&P Global Composite PMI fell slightly to 54.1 in August's flash estimate from 54.3 in July, better than the expectation of 53.5. Meanwhile, Manufacturing PMI dropped to 48 in the same period from 49.6. Services PMI rose to 55.2 in August versus 55 prior.
- Federal Reserve Bank of Boston President Susan Collins stated that it will soon be appropriate to begin cutting rates, adding that incoming data will guide the pace of rate cuts.
- Kansas City Fed President Jeff Schmid noted Thursday that he was looking more closely at the dynamics behind the increase in the unemployment rate and would let data guide his decision on whether to support a rate reduction next month.
- Investors are now pricing in around 76% odds of a 25 basis points (bps) Fed rate cut in its September meeting, according to the CME FedWatch Tool.
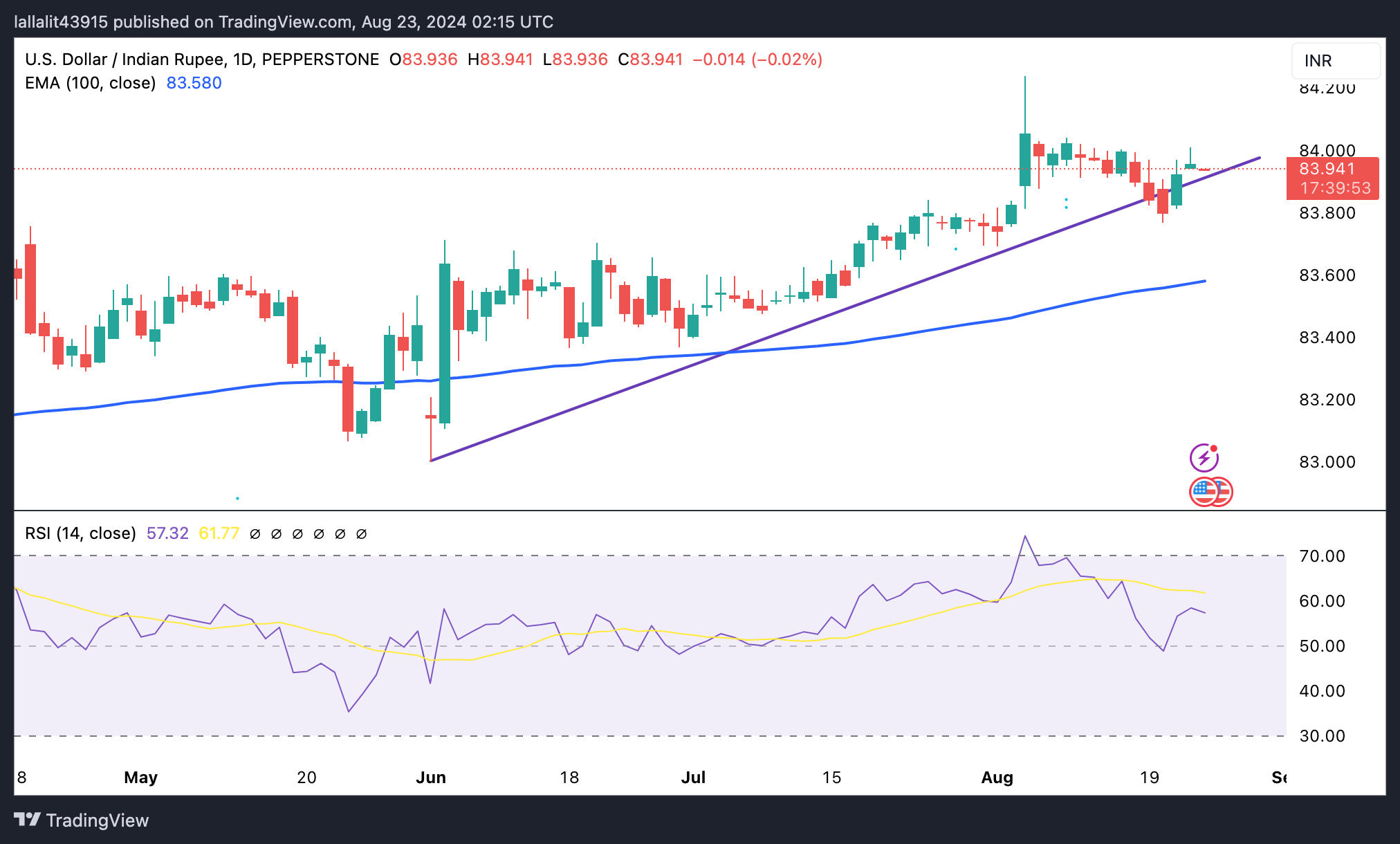
Technical Analysis: USD/INR’s constructive outlook remains in place
Indian Rupee trades firmer on the day. The most notable feature of the USD/INR pair is the strong uptrend as the price remains above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and the 11-week-old uptrend line. Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) points higher above the midline near 58.40, suggesting that the bullish momentum is sustained.
If USD/INR pops up bullish pressure above the 84.00 psychological mark, the pair could retest the record high of 84.24. A decisive break above this level may attract buyers to 84.50.
Sustained trading below the ascending trendline around 83.92 could draw in sellers and drag the pair to 83.77, the low of August 20. The next contention level to watch is the 100-day EMA at 83.57.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.















