- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- Mexican Peso registers losses against US Dollar after mixed US data
Mexican Peso registers losses against US Dollar after mixed US data
- Mexican Peso dips to 16.69 against US Dollar in early North American session.
- US Initial Jobless Claims rise above forecasts, mixed housing data with Building Permits down and Housing Starts up.
- Fed officials signal patience on inflation target amid potential rate cuts in 2024.
The Mexican Peso registered some losses against the US Dollar in early trading during the North American session on Thursday. The Mexican currency capitalized on a United States (US) inflation report that increased the possibility of rate cuts by the Federal Reserve (Fed) in 2024. At the time of writing, the USD/MXN trades at 16.69, up 0.04%.
The USD/MXN continued to lean on US economic data amid an absent Mexican economic docket. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revealed that the number of Americans filing for unemployment insurance grew above the previous reading and exceeded forecasts.
At the same time, housing data revealed mixed figures. Building Permits missed the mark, while Housing Stars recovered in April after posting disappointing figures in March.
In the meantime, the Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Index clung to expansionary levels but continued to deteriorate, while Industrial Production remained unchanged.
Recently, Fed officials crossed the wires. Richmond Fed President Thomas Barkin stated that inflation is coming down, but that it will “take more time,” to hit the Fed’s target. Cleveland Fed President Loretta Mester welcomed the latest CPI data, adding that monetary policy is well-positioned as the Fed reviews upcoming data.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso surges on soft US CPI, disappointing Retail Sales
- Mexico’s economic docket will be absent during the current week. The next economic data release is expected to be Retail Sales on May 20, followed by the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation figures and Banxico’s minutes on May 23.
- April's data show that Mexico’s headline inflation is reaccelerating. However, core prices are falling. This spurred Banxico’s revision to its inflation projections, with the bank expected to hit its 3% target toward the last quarter of 2025, later than March’s estimates for Q2 2025. Core inflation is projected to hit 3% in Q2 2025.
- The US Department of Labor revealed the labor market is cooling as Initial Jobless Claims for the latest week came in above forecasts at 222K in the week ending May 11, below the previous reading of 232K but exceeding forecasts of 220K.
- US Housing Starts increased to 1.36 million or 5.7% YoY in April, revealed government data. Building Permits, a proxy for future construction, dropped 3% to a 1.44 million rate.
- Investors have become optimistic that the Fed may cut rates this year after US inflation data showed the downtrend is resuming, while Retail Sales remained unchanged.
- Data from the CME FedWatch Tool shows odds for a 25 bps rate cut at the September meeting remain at 87%, higher than Tuesday's 83%.
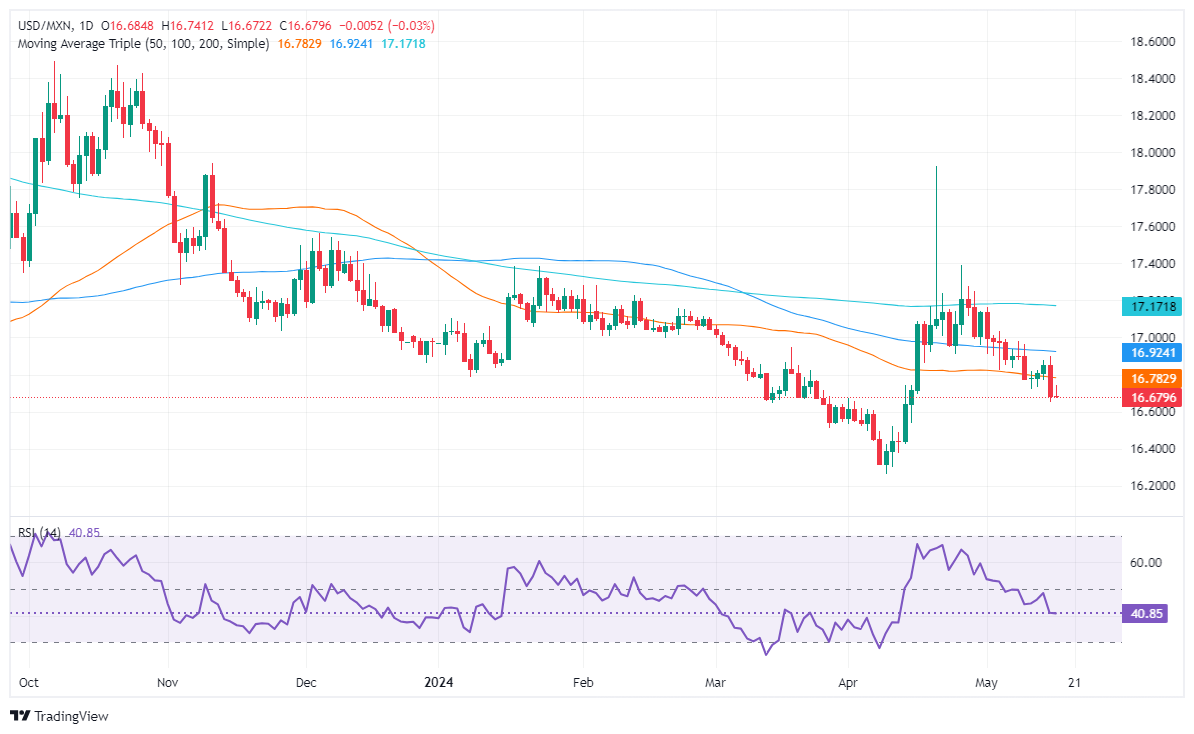
Technical analysis: Mexican Peso on the defensive as USD/MXN rises above 16.67
The USD/MXN downtrend continues even though buyers pushed the exchange rate past close to the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) near 16.78. Momentum is on the side of the Mexican Peso as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) remains in bearish territory, aiming toward oversold territory.
If USD/MXN extends its losses beneath last year’s low of 16.62, that could exacerbate a 16.50 test ahead of the current year-to-date low of 16.25.
Conversely, if buyers reclaim the 50-day SMA at 16.78, it could exacerbate a rally toward the 100-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 16.92. Once cleared, the next supply zone would be the 17.00 psychological level. In that event, the next stop would be the 200-day SMA at 17.17.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.