- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- Dow Jones Industrial Average falls back after US GDP flubs expectations but inflation still hot
Dow Jones Industrial Average falls back after US GDP flubs expectations but inflation still hot
- Dow Jones backslides over 500 points as investors balk at inflation complications.
- US GDP eased quicker than expected, jostling risk appetite.
- Equity recovery is under way, but remains limited.
The Dow Jones hit its lowest bids in a week after US Gross Domestic Product (GDP) figures missed forecasts and US Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) inflation came in higher than expected. Slowing growth is a boon for investors seeking an accelerated path towards rate cuts from the Federal Reserve (Fed), but sticky inflation continues to vex hopes for an early Fed rate trim.
Read more: US GDP expands less that expected in Q1
US GDP for the annualized first quarter grew by 1.6%, well below the forecast decline to 2.5% from the previous 3.4%. It represents the slowest pace of GDP growth since September of 2022, but an uptick in Core PCE in Q1 kicked the legs out from beneath rate cut hopes. Q1 Core PCE rebounded to 3.7%, climbing over the previous 2.0% and overshooting the forecast 3.4%. Headline PCE inflation also overshot, printing at 3.4% versus the previous 1.8% as inflation remains hotter than investors hoped.
Dow Jones news
The Dow Jones plunged into negative territory for the week, knocking below 37,800.00 and declining over 550 points on the sour US data prints. A slow, grinding equity recovery is underway in the US trading session, but the Dow Jones remains firmly off of the day’s early peak bids near 38,450.00.
Around two-thirds of the individual securities that comprise the Dow Jones are in the red on Thursday, with International Business Machines Corp. (IMB) leading the charge down. IBM is down over 8% at the time of writing, declining to $168.77 per share. IBM is closely followed by Caterpillar Inc. (CAT), down around 6.5% on the day and trading near $340.12. The DJIA’s top gainer on Thursday is Merck & Co Inc. (MRK), climbing nearly 3% to trade into $130.63 per share.
Dow Jones technical outlook
The Dow Jones declined 1.82% top-to-bottom on Thursday, hitting a seven-day low of 37,745.54 and turning negative for the week. Despite the major equity index reclaiming nearly half of the day’s declines, the DJIA remains well back from the day’s peaks at 38,446.43.
Despite the Dow Jones on pace for a second down day in a row, the index is still firmly planted in bull country, trading well above the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 36,700.41.
Dow Jones five-minute chart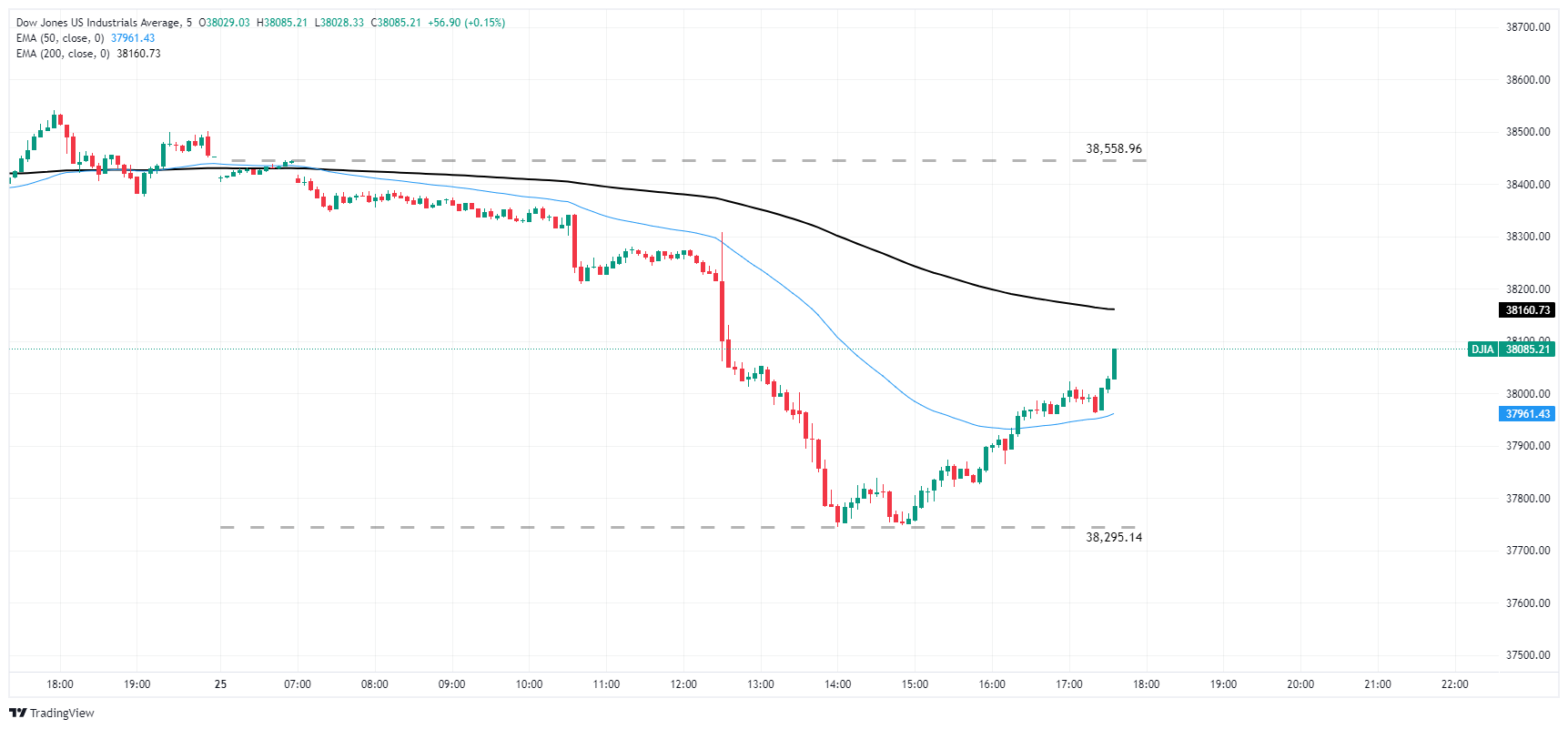
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.















