- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- Australian Dollar gains ground on softer US Dollar amid weaker Aussie data
Australian Dollar gains ground on softer US Dollar amid weaker Aussie data
- Australian Dollar recovers the recent losses as the Greenback struggles to hold ground.
- Australia’s Private Capital Expenditure declined by 0.6% in Q3, against the expected rise of 1.0%.
- US GDP Annualized increased by 5.2% as compared to the 4.9% prior.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) attempts to recover the recent losses, despite downbeat economic data from Australia on Thursday. The AUD/USD pair retraced from its nearly four-month high at 0.6676 in the previous session. The downward pressure on the Aussie pair can be attributed to the recovery in strength of the US Dollar (USD).
Australia's Private Capital Expenditure experienced a decline of 0.6% in Q3, contrasting with the previous growth of 2.8%. This contraction fell short of the expected rise of 1.0%. The data, released by the Australian Bureau of Statistics, indicates a decrease in both current and future capital expenditure intentions within the private sector of the country. This could ease the inflationary pressure, which reduces the likelihood of an interest rate hike by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
The US Dollar Index (DXY) managed to halt its four-day losing streak on Wednesday. This stabilization was supported by stronger-than-expected US Gross Domestic Product Annualized data released by the US Bureau of Economic Analysis. The US GDP data indicated an increase in the value of the final goods and services produced in the United States during the third quarter. However, the index struggles to maintain its position on Thursday.
United States is set to release crucial economic data later in the North American session. Among the notable reports are the weekly Jobless Claims for the week ending on November 24, with an expected increase to 220K from the previous 209K. Additionally, the Core Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index for October will be released, with expectations of a slowdown in consumer inflation. The anticipated annual rate is expected to decrease from 3.7% to 3.5%.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Australian Dollar receives upward support amid hawkish RBA
- Australia's Monthly Consumer Price Index (CPI) for October shows a reading of 4.9%, a decrease from the previous reading of 5.6% in September and slightly below the expected 5.2%.
- Australia’s seasonally adjusted Retail Sales data showed monthly readings for October, which declined by 0.2% against the market expectations of a 0.1% rise and 0.9% prior.
- Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) Governor Michele Bullock highlighted that the current monetary policy is on the restrictive side, with rate hikes putting a damper on demand, particularly in the context of persistent services inflation.
- Governor Bullock emphasized the need for caution in employing high interest rates to combat inflation without inadvertently raising the unemployment rate.
- US Federal Reserve Governor Christopher Waller suggested that if inflation consistently declines, there's no need to maintain high-interest rates.
- US Gross Domestic Product Annualized increased by 5.2% during the third quarter from the previous reading of 4.9%, above the market consensus of 5.0.
- US Housing Price Index (MoM) remained consistent at 0.6% in September against the expected figure of 0.4%.
- The CB Consumer Confidence Index experienced an increase in November, rising to 102.0. This uptick comes after a downward revision of October figures, which were adjusted from 102.6 to 99.1.
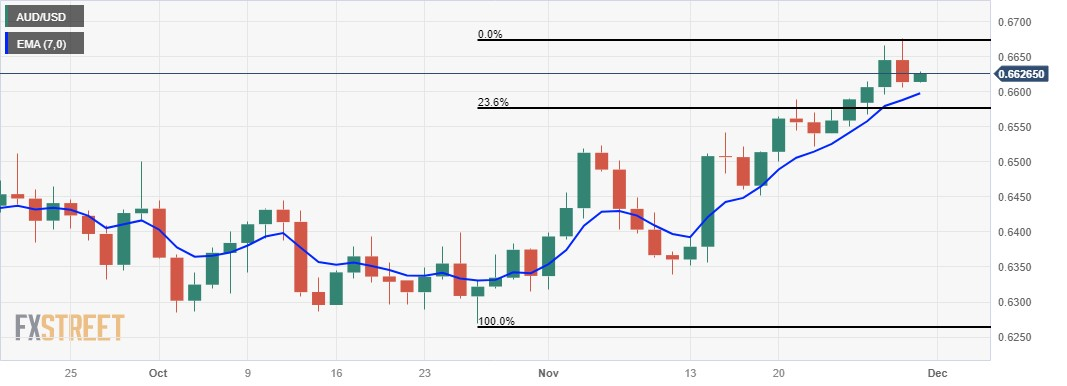
Technical Analysis: Australian Dollar hovers below the barrier at 0.6650 major level
The Australian Dollar trades at higher levels, approximately around 0.6630 on Thursday. The major level at 0.6650 could be the immediate resistance, followed by a significant barrier at the psychological level of 0.6700. A successful breakthrough above this level may provide support for the AUD/USD pair, opening the possibility of testing the resistance around August's high at 0.6723. Conversely, key support is positioned around the seven-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 0.6597. A decisive break below the EMA could potentially lead the pair to reach support near the 23.6% Fibonacci retracement level at 0.6576, followed by the major level at 0.6550.
AUD/USD: Daily Chart
Australian Dollar price today
The table below shows the percentage change of Australian Dollar (AUD) against listed major currencies today. Australian Dollar was the strongest against the Japanese Yen.
| USD | EUR | GBP | CAD | AUD | JPY | NZD | CHF | |
| USD | -0.05% | 0.00% | -0.03% | -0.10% | 0.02% | -0.24% | -0.10% | |
| EUR | 0.05% | 0.03% | 0.01% | -0.07% | 0.08% | -0.20% | -0.07% | |
| GBP | 0.00% | -0.04% | -0.02% | -0.10% | 0.04% | -0.23% | -0.09% | |
| CAD | 0.03% | -0.02% | 0.03% | -0.08% | 0.05% | -0.21% | -0.07% | |
| AUD | 0.07% | 0.07% | 0.10% | 0.08% | 0.13% | -0.16% | 0.00% | |
| JPY | -0.03% | -0.06% | -0.05% | -0.04% | -0.15% | -0.25% | -0.12% | |
| NZD | 0.23% | 0.19% | 0.22% | 0.21% | 0.14% | 0.25% | 0.13% | |
| CHF | 0.11% | 0.05% | 0.09% | 0.07% | 0.00% | 0.11% | -0.13% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/JPY (quote).
Australian Dollar FAQs
What key factors drive the Australian Dollar?
One of the most significant factors for the Australian Dollar (AUD) is the level of interest rates set by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA). Because Australia is a resource-rich country another key driver is the price of its biggest export, Iron Ore. The health of the Chinese economy, its largest trading partner, is a factor, as well as inflation in Australia, its growth rate and Trade Balance. Market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – is also a factor, with risk-on positive for AUD.
How do the decisions of the Reserve Bank of Australia impact the Australian Dollar?
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) influences the Australian Dollar (AUD) by setting the level of interest rates that Australian banks can lend to each other. This influences the level of interest rates in the economy as a whole. The main goal of the RBA is to maintain a stable inflation rate of 2-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively high interest rates compared to other major central banks support the AUD, and the opposite for relatively low. The RBA can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former AUD-negative and the latter AUD-positive.
How does the health of the Chinese Economy impact the Australian Dollar?
China is Australia’s largest trading partner so the health of the Chinese economy is a major influence on the value of the Australian Dollar (AUD). When the Chinese economy is doing well it purchases more raw materials, goods and services from Australia, lifting demand for the AUD, and pushing up its value. The opposite is the case when the Chinese economy is not growing as fast as expected. Positive or negative surprises in Chinese growth data, therefore, often have a direct impact on the Australian Dollar and its pairs.
How does the price of Iron Ore impact the Australian Dollar?
Iron Ore is Australia’s largest export, accounting for $118 billion a year according to data from 2021, with China as its primary destination. The price of Iron Ore, therefore, can be a driver of the Australian Dollar. Generally, if the price of Iron Ore rises, AUD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Iron Ore falls. Higher Iron Ore prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance for Australia, which is also positive of the AUD.
How does the Trade Balance impact the Australian Dollar?
The Trade Balance, which is the difference between what a country earns from its exports versus what it pays for its imports, is another factor that can influence the value of the Australian Dollar. If Australia produces highly sought after exports, then its currency will gain in value purely from the surplus demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase its exports versus what it spends to purchase imports. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens the AUD, with the opposite effect if the Trade Balance is negative.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.















