- Analytics
- News and Tools
- Market News
- Euro gathers fresh traction above 1.1000
Euro gathers fresh traction above 1.1000
- Euro adds to Friday’s advance above 1.1000 against the US Dollar.
- Stocks in Europe open Monday’s session in a mixed tone.
- EUR/USD looks to regain further ground beyond 1.1000 the figure.
- EMU Flash headline Inflation Rate extended the downward trend in July.
- Germany’s Retail Sales contracted 1.6% YoY in June.
The Euro (EUR) is continuing to maintain its recovery against the US Dollar (USD) that began on Friday, which is causing EUR/USD to extend its upward trend after breaking through the important 1.1000 level at the start of the week.
The pair gained momentum after hitting a low of around 1.0940 on Friday, as the Greenback was undergoing a corrective move.
Currently, both US and European yields are trading with uncertainty, as investors are still digesting last week's interest rate decisions by the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank (ECB).
Regarding the ECB, President Christine Lagarde has indicated that the central bank is keeping an "open-minded" approach to the upcoming September meeting and emphasized that the future rate decisions will depend on economic data. Similarly, Fed Chair Jerome Powell has reiterated multiple times that the Fed's decisions on rates will be data-dependent at the FOMC event on July 26.
In terms of speculative positioning, the net longs in EUR have remained relatively unchanged in the week ending on July 25th according to CFTC, which was prior to the FOMC and ECB gatherings. During this time, spot had retreated from yearly highs around 1.1275 (July 18) to the low 1.1000s.
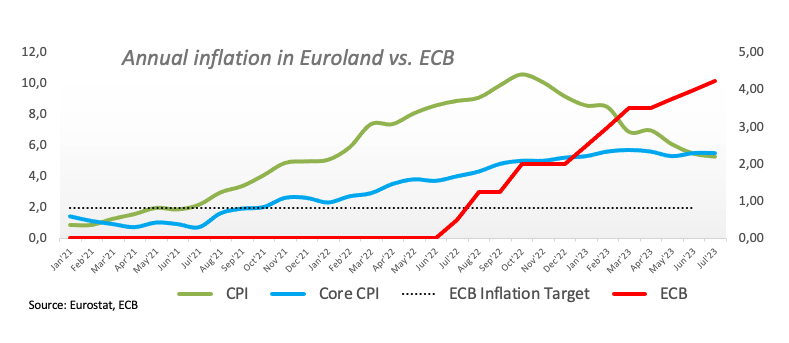
In the Eurozone, Germany's Retail Sales declined by 1.6% YoY in June, and Italian Q2 GDP Growth Rate was lower than expected, with a QoQ contraction of 0.3% and YoY expansion of 0.6%. Additionally, preliminary inflation figures in the Euro area show that the Core CPI rose more than anticipated, by 5.5% YoY in July and 5.3% YoY in headline CPI. Finally, the flash Q2 GDP Growth Rate for the bloc shows that the economy expanded by 0.3% QoQ and 0.6% YoY.
There are no significant data releases scheduled in the US docket for Monday.
Daily digest market movers: Euro keeps the rebound well in place
- The EUR picks up pace above the 1.1000 mark vs. the USD.
- The USD Index treads water around 101.70 on Monday.
- EMU flash GDP figures surprise to the upside in Q2.
- Core inflation in the euro area remains sticky.
- US, German yields trade without direction across all maturities.
- The Italian economy is expected to have contracted slightly in Q2.
- Markets’ attention is expected to be on the US labour market this week.
Technical Analysis: Euro faces a minor hurdle at 1.1150
EUR/USD manages to gather some impulse and extend the bounce off recent lows north of the 1.1000 hurdle so far on Monday.
If bears regain the upper hand, EUR/USD should put the weekly low of 1.0943 (July 28) to the test ahead of a probable move to the transitory 55-day and 100-day SMAs at 1.0908 and 1.0906, respectively. The loss of this region could open the door to a potential visit to the July low of 1.0833 (July 6) ahead of the key 200-day SMA at 1.0723 and the May low of 1.0635 (May 31). South from here emerges the March low of 1.0516 (March 15) before the 2023 low of 1.0481 (January 6).
On the other hand, occasional bullish attempts could motivate the pair to initially dispute the weekly top at 1.1149 (July 27). Above this level the downside pressure could mitigate somewhat and could encourage the pair to test the 2023 high at 1.1275 (July 18). Once this level is cleared, there are no resistance levels of significance until the 2022 peak of 1.1495 (February 10), which is closely followed by the round level of 1.1500.
Furthermore, the constructive view of EUR/USD appears unchanged as long as the pair trades above the key 200-day SMA.
Euro FAQs
What is the Euro?
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day.
EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
What is the ECB and how does it impact the Euro?
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy.
The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa.
The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
How does inflation data impact the value of the Euro?
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control.
Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
How does economic data influence the value of the Euro?
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency.
A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall.
Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
How does the Trade Balance impact the Euro?
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period.
If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
© 2000-2026. All rights reserved.
This site is managed by Teletrade D.J. LLC 2351 LLC 2022 (Euro House, Richmond Hill Road, Kingstown, VC0100, St. Vincent and the Grenadines).
The information on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice.
The company does not serve or provide services to customers who are residents of the US, Canada, Iran, The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Yemen and FATF blacklisted countries.
Making transactions on financial markets with marginal financial instruments opens up wide possibilities and allows investors who are willing to take risks to earn high profits, carrying a potentially high risk of losses at the same time. Therefore you should responsibly approach the issue of choosing the appropriate investment strategy, taking the available resources into account, before starting trading.
Use of the information: full or partial use of materials from this website must always be referenced to TeleTrade as the source of information. Use of the materials on the Internet must be accompanied by a hyperlink to teletrade.org. Automatic import of materials and information from this website is prohibited.
Please contact our PR department if you have any questions or need assistance at pr@teletrade.global.















